Noise Figure for 2-Port Networks
In electronic engineering, understanding noise figure is paramount, especially when it comes to designing communication systems and amplifiers. In a 2-port network, noise figure plays a pivotal role in determining the system’s overall noise performance. Let’s delve deeper into the intricacies of noise figure and explore the trade-offs between power matching and noise optimization.
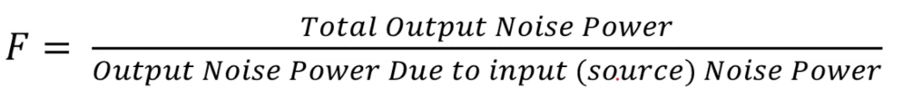
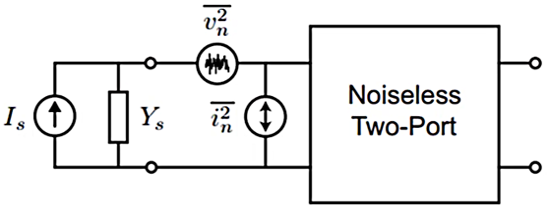
Noise figure serves as a vital metric for assessing the noise performance of electronic components, particularly in devices where maintaining high sensitivity and signal quality is crucial. In applications like radio receivers, radar systems, and wireless communication networks, minimizing noise figure is essential for maximizing the system’s ability to detect and process weak signals amidst background noise.
Low Noise Amplifiers (LNAs): LNAs are pivotal components in communication systems, tasked with amplifying weak signals while introducing minimal additional noise. The noise figure of an LNA directly impacts the overall sensitivity and signal-to-noise ratio of the system. By optimizing the noise figure of LNAs, engineers can enhance the system’s ability to detect and amplify faint signals, thereby improving its performance in low signal strength environments.
Mixers: Mixers are essential in frequency conversion and signal modulation/demodulation processes. The noise figure of a mixer affects the conversion efficiency and fidelity of the modulated signal. Minimizing the noise figure ensures that the mixer introduces minimal additional noise during the frequency conversion process, thereby preserving the integrity of the modulated signal.
Receivers: In receivers, which are tasked with capturing, demodulating, and processing incoming signals, noise figure plays a critical role in determining the system’s overall sensitivity and noise performance. A receiver with a low noise figure can effectively amplify weak signals while maintaining a high signal-to-noise ratio, enabling reliable communication and data transmission even in noisy environments.
Defining Noise Figure
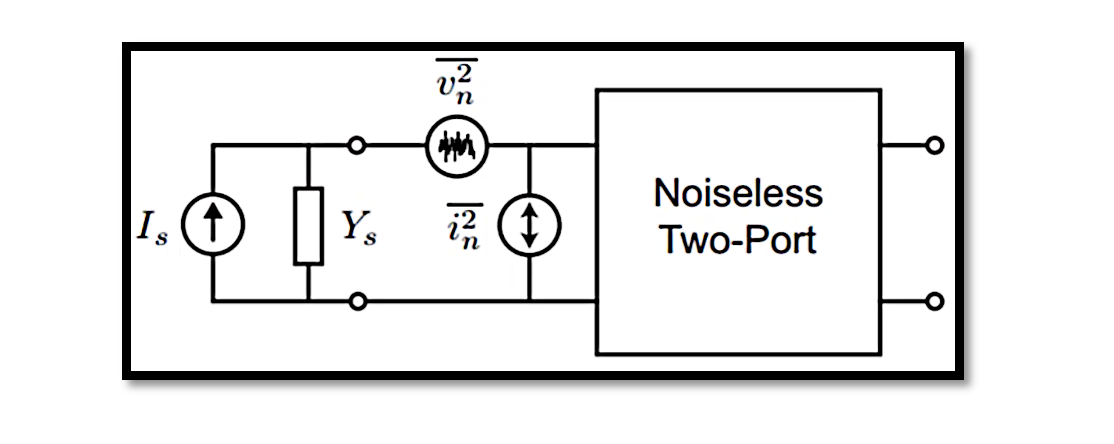
Noise figure (F) is a key parameter that quantifies the amount of noise added by a device to the signal passing through it. It is expressed as the ratio of the total output noise power to the output noise power due to input (source) noise power:
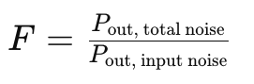
Power Matching vs. Noise Optimization
One fundamental aspect of noise figure in 2-port networks is the trade-off between power matching and minimum noise. Ideally, we aim for power matching between the source and the input of the device to maximize power transfer efficiency. However, achieving power matching doesn’t necessarily guarantee optimal noise performance.
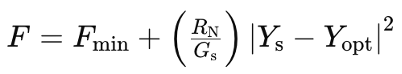
Ys,opt ≠ Yin
It’s essential to note that in general, the optimum source admittance (Ys,opt) does not equal the input admittance (Yin). This implies that achieving noise match doesn’t automatically correspond to gain match. As a result, engineers often face a dilemma where they must strike a balance between power matching and noise optimization.
Transistor Characteristics
The noise figure of a device is influenced by various factors, including the intrinsic noise resistance (RN) and conductance (Gs) of the transistor. Transistors with lower RN values are preferable as they contribute less noise to the system, leading to lower noise figures.
Finding the Optimal Performance
In real-world scenarios, finding the optimal balance between power matching and noise performance is crucial. This often involves making compromises to ensure that the system achieves satisfactory noise performance without sacrificing significant power transfer efficiency.
Implications for System Design
Understanding the intricacies of noise figure in 2-port networks has profound implications for system design. Engineers must carefully consider factors such as impedance matching, transistor characteristics, and trade-offs between noise performance and gain. By doing so, they can design systems that offer improved sensitivity, signal integrity, and overall performance.
Conclusion
Noise figure is a critical parameter in the design of electronic circuits, particularly in communication systems and amplifiers. In 2-port networks, achieving optimal noise performance involves navigating the delicate balance between power matching and noise optimization. By understanding the trade-offs involved and carefully designing systems with these considerations in mind, engineers can develop high-performance electronic circuits with enhanced noise characteristics.
Tag:LNA Design, Noise Figure