Introduction to Power Amplifiers: Understanding the Fundamentals
These devices form an integral part of modern electronics, serving to increase the power of a signal for various applications. Understanding their fundamentals is key to comprehending their significance in today’s technology-driven world.
Power Amplifiers
At its core, a power amplifier is designed to boost the power level of an input signal without distorting its waveform significantly. This amplified signal is crucial in scenarios where the original signal lacks the necessary strength to drive a load, such as speakers or antennas.
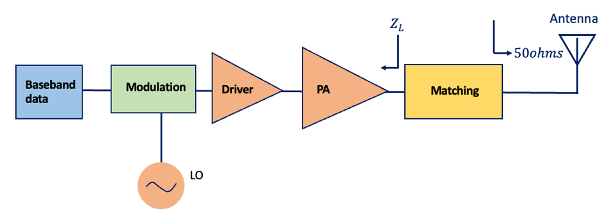
Fundamentals of Power Amplification
The process of power amplification involves taking a low-power signal and increasing its amplitude while retaining the essential characteristics of the original signal. This amplification is achieved through various techniques, often utilizing electronic components like transistors or vacuum tubes. Understanding the amplification process involves delving into concepts like gain, linearity, and efficiency. Gain refers to the ratio of output power to input power, while linearity ensures that the amplified signal maintains fidelity to the original input. Efficiency measures how effectively the amplifier converts input power into output power without unnecessary losses.
Read about RF Receiver Architecture and Channel Selection
Types of Power Amplifiers
Power amplifiers come in different types based on their application and the nature of signals they amplify. Broadly categorized, they can be:
- Analog vs. Digital Amplifiers: Analog amplifiers amplify continuous signals, while digital amplifiers convert analog signals into digital form before amplification.
- Classes of Amplifiers: They are classified into classes like Class A, B, AB, and D, each with its unique characteristics of efficiency, linearity, and distortion.
- Radio Frequency (RF) Power Amplifiers: These specifically amplify RF signals used in wireless communications, broadcasting, radar systems, and more. They demand specialized designs due to their high frequencies and stringent requirements.
Exploring Various Types and Applications of RF Power Amplifiers
RF Power Amplifiers: A Closer Look
RF power amplifiers hold a crucial position in wireless communication systems. They are tailored to amplify radio frequency signals used for transmitting information wirelessly over considerable distances.
Types of RF Power Amplifiers
- Class A RF Amplifiers: Known for their linearity but low efficiency.
- Class B and AB RF Amplifiers: Improved efficiency but with some trade-offs in linearity.
- Class C RF Amplifiers: High efficiency but used where linearity is less critical, like in RF transmitters.
- Class D RF Amplifiers: Also known as switching amplifiers, they offer high efficiency but are more complex in design.
Applications of RF Power Amplifiers
RF power amplifiers find applications in diverse fields:
- Wireless Communication: Cell phones, Wi-Fi routers, satellite communication systems, and more rely on RF power amplifiers for signal transmission.
- Broadcasting: Radio and television broadcasting stations utilize high-power RF amplifiers for signal transmission.
- Radar Systems: Radar technology, used in aviation, weather forecasting, and military applications, employs RF power amplifiers for signal amplification.
Understanding power amplifiers, particularly RF amplifiers, unveils their significance in enabling our interconnected world. Their advancements continue to drive innovations in wireless communication, broadcasting, and various other domains. Stay tuned for deeper dives into specific amplifier types and their evolving role in shaping modern technology!
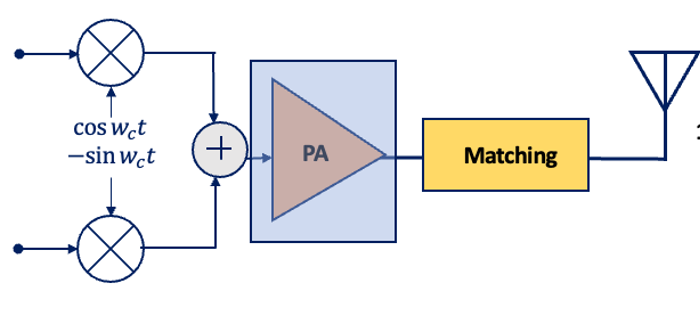
Technical Insights into Power Amplifiers in Transmitters
Power amplifiers (PAs) within transmitters are the workhorses that elevate low-power signals to levels suitable for efficient transmission across vast distances. Delving into their technical intricacies unveils a world of amplification mechanisms and optimization strategies.
Signal Amplification and Gain
At the heart of power amplifiers lies the concept of gain, often represented in decibels (dB). The gain (G) of an amplifier can be calculated using the formula:
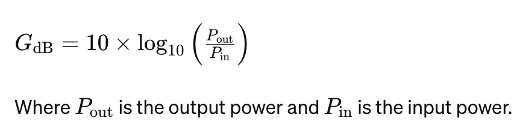
Efficiency and Power Dissipation
Efficiency (η) in power amplifiers determines the ratio of output power to input power and is crucial in minimizing energy wastage. It can be calculated using the formula:

Amplifier Classes and Characteristics
Power amplifiers fall into different classes (A, B, AB, C) each with unique operating characteristics. Class A amplifiers, for instance, provide high linearity but are less efficient compared to Class B or AB amplifiers. The efficiency (η) of an amplifier can be determined using its supply voltage (Vcc) and quiescent current (Iq) by the formula:
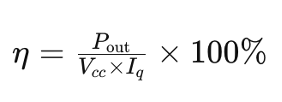
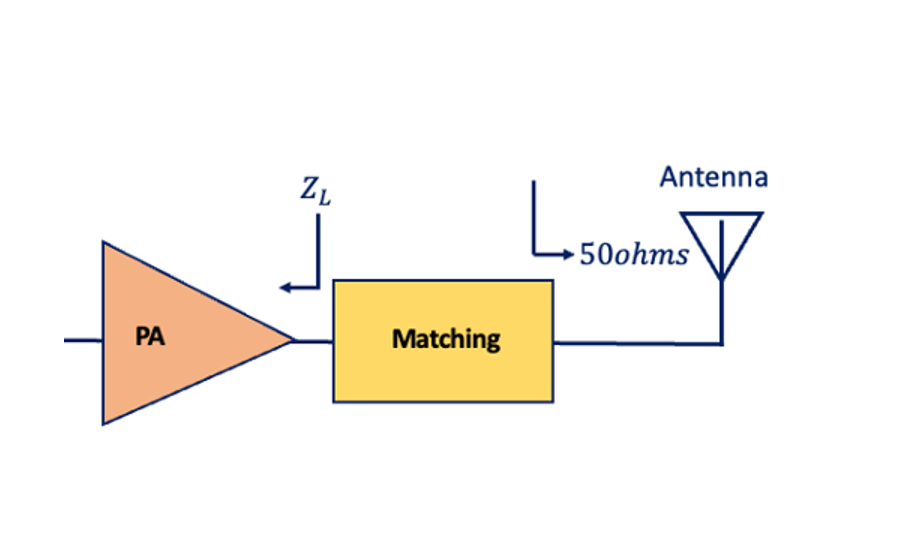
RF Power Amplifiers and Matching Networks
RF power amplifiers are tailored for radio frequency signals and require matching networks to optimize power transfer. The relationship between input impedance (Zin) and output impedance (Zout) can be crucial for maximizing power transfer efficiency and minimizing signal reflections.
Power Gain and Maximum Power Transfer Theorem
The power gain (Gp) of an amplifier, considering the maximum power transfer theorem, is obtained when the input and output impedances are conjugate matched:
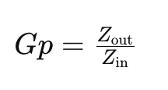
Heat Dissipation and Thermal Management
To prevent component damage due to excess heat, heat dissipation (Pheat) should be managed effectively. Heat dissipation can be calculated using various thermal resistance and power handling characteristics of the amplifier components.
Understanding these technical aspects allows engineers to design and optimize power amplifiers for specific applications, balancing trade-offs between gain, efficiency, linearity, and heat management. In the intricate world of power amplifiers within transmitters, these formulas and concepts serve as guiding principles for engineers striving to enhance the performance and efficiency of communication systems, ensuring robust and reliable signal transmission across diverse communication channels.

Learn more about more topic like this. Browse various RF course on our website and watch the course videos for more detailed understanding https://rahsoft.com/courses/. Rahsoft also provides a certificate on Radio Frequency. All the courses offer step by step approach.