Exploring the Applications of RF Attenuators
Introduction:
RF attenuators, often overlooked but indispensable in the realm of radio frequency engineering, are versatile tools with a spectrum of applications across various domains. Their ability to finely adjust signal levels makes them invaluable in managing RF systems, safeguarding sensitive equipment, and ensuring accurate measurements. This blog aims to delve into the multifaceted applications of RF attenuators, uncovering their pivotal role in signal control, equipment protection, system optimization, and beyond. From fine-tuning signal strengths for precise testing to mitigating interference and enhancing system performance, the versatility of attenuators shapes the landscape of RF engineering in myriad ways.
Utilizing RF Attenuators in Signal Control and Equipment Protection
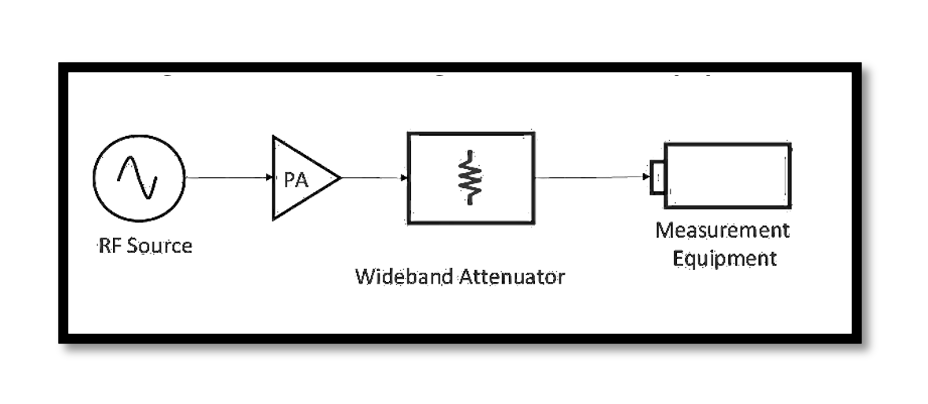
In various RF applications, the utilization of attenuators offers a flexible approach to managing signal levels to suit specific needs. One fundamental application involves regulating the power level of an RF stage preceding another component. While it may seem counterintuitive to attenuate a signal, especially when efficiency is a concern, there are scenarios where this adjustment becomes crucial. Consider a situation where testing power amplifiers is the primary task. Picture an RF setup comprising an RF source, a power amplifier, a wideband attenuator, and measurement equipment. The attenuator, in this context, plays a pivotal role in fine-tuning the power level, ensuring optimal testing conditions for the amplifiers. Moreover, attenuators often serve a protective function for sensitive equipment incapable of handling high-power inputs.
Take, for instance, the aforementioned measurement equipment in the setup. It might lack the capacity to tolerate the maximum output power emanating from the power amplifier. In such cases, employing an attenuator becomes imperative to mitigate the risk of equipment damage. By attenuating the signal, the attenuator acts as a shield, safeguarding the measurement equipment from potential harm, thereby enabling accurate and safe signal measurements.
Enhancing Receiver Sensitivity and Noise Mitigation using Attenuators
Deploying attenuators in specific applications involving low-power requirements, such as in receiver setups, presents an intricate yet crucial solution. Consider scenarios where receiver performance hinges on its ability to detect signals amidst low power levels, even bordering on the noise floor. Evaluating the receiver’s reference sensitivity level demands assurance that it can reliably capture and process signals at these exceptionally low power levels. Complications arise when extraneous noise infiltrates the setup, potentially stemming from various sources like improperly terminated ports or RF cables acting as unintended antennas for certain frequencies. This interference can disrupt testing procedures, misleadingly suggesting receiver malfunction due to its inability to demodulate signals from the vector signal generator.
To counter such challenges, integrating an attenuator becomes paramount. Despite the common knowledge that attenuators primarily reduce signal strength, in this context, their purpose shifts. By incorporating an attenuator strategically within the setup, its role becomes pivotal in augmenting the power level of the preceding RF stage. How does this reversal occur when attenuators are conventionally known for signal reduction?
The process involves compensating for the elements between the vector signal generator and the receiver. For instance, adding a 10dB attenuator necessitates a compensatory 10dB increase in the RF signal before it reaches the receiver. Consequently, while the attenuator doesn’t amplify the signal per se, it mandates an escalation in power at the previous stage, namely the vector signal generator. This amplification cascades, resulting in an improved signal-to-noise ratio. Despite potential interference, the impact is mitigated due to the amplified desired signal, making the unwanted noise comparatively less disruptive.
Placing the attenuator in close proximity to the receiver proves pivotal, as it effectively attenuates the noise sources coupling into the setup. This strategic placement ensures that while the signal from the vector signal generator is elevated, the unwanted noise remains relatively constant. The enhanced signal-to-noise ratio facilitates effective noise reduction, permitting accurate receiver testing. The application of attenuators in such scenarios highlights their versatility, adaptable to various setups and dependent on specific application needs. Attenuators come in an array of attenuation steps, ranging from as low as 1dB or 2dB to as high as 200dB, catering to diverse use cases and application requirements.
More Applications of RF Attenuators
Signal Integrity in Testing Environments
In test setups where signal integrity is paramount, RF attenuators play a crucial role in ensuring accurate measurements and evaluations. When testing sensitive components or systems, maintaining signal integrity becomes challenging, especially in scenarios where signal reflections, mismatched impedance, or excessive power levels might occur. Attenuators effectively address these issues by managing signal levels, minimizing reflections, and preventing equipment damage or inaccuracies caused by signal overload.
Antenna Testing and Calibration
Antenna testing often requires precise control of signal levels to simulate real-world conditions accurately. Attenuators enable engineers to fine-tune the signal strength applied to antennas during testing, allowing for the calibration of antenna systems across various frequency ranges. This calibration ensures that antennas perform optimally under different signal strengths, aiding in the development and validation of antenna designs for specific applications.
Transmitter Power Adjustment
In transmitter systems, maintaining compliance with regulatory power output limits is crucial. Attenuators are instrumental in adjusting transmitter power levels to ensure adherence to legal requirements. By strategically placing attenuators in the RF chain, engineers can precisely control and limit the output power, preventing excessive transmission that could interfere with other systems or violate regulatory standards.
Noise Figure Measurements
Measuring noise figure accurately in RF systems is essential for assessing their sensitivity and performance. Attenuators assist in controlling signal levels during noise figure measurements, enabling engineers to characterize the noise characteristics of amplifiers, receivers, and other components. By precisely adjusting signal levels using attenuators, accurate noise figure measurements can be obtained, aiding in system optimization and troubleshooting.
Conclusion:
In the intricate world of RF engineering, where signal precision, system reliability, and accurate measurements reign supreme, the often-underestimated RF attenuators emerge as unsung heroes. Their applications extend far beyond mere signal reduction; they serve as guardians of sensitive equipment, architects of signal integrity, and enablers of precise testing environments. From calibrating antennas to fine-tuning transmitter power and balancing system gains, the versatility of RF attenuators illuminates their significance in every facet of RF system design, testing, and optimization. As technology advances and RF systems evolve, the role of these unassuming devices continues to expand, shaping the landscape of RF engineering and reinforcing their status as indispensable tools in the engineer’s arsenal.

Learn more about this topic by taking the complete course ‘Introduction to RF Testing Fundamentals and RF Test Architecture – RAHRF412’. Watch the course videos for more detailed understanding. Also checkout other courses on RF system and IC design on https://rahsoft.com/courses/. Rahsoft also provides a certificate on Radio Frequency. All the courses offer step by step approach.