Understanding Carrier Waves
In electronic communication, a carrier wave is a waveform that is used to transmit information. This wave, also known as a carrier signal or simply a carrier, is typically of a much higher frequency than the information or message signal it carries. Carrier waves can be thought of as a “vehicle” that transports information from one point to another. By modulating (altering) certain properties of the carrier wave with the input data or message signal, we can convey data efficiently over different media, such as air, cables, or fiber optics.
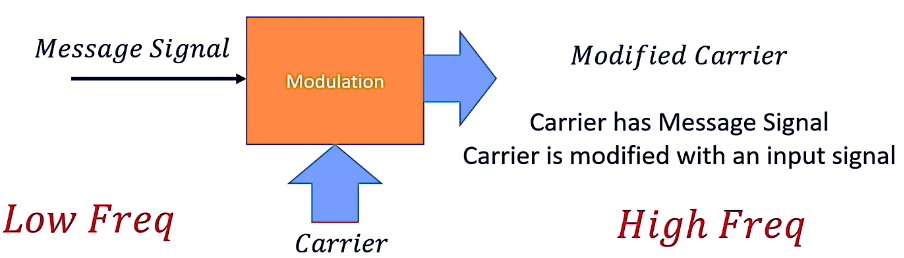
Key Concepts in Modulation
1. Carrier Wave Characteristics
- A carrier wave is often a high-frequency signal with properties that can be adjusted to carry information.
- These properties include amplitude, phase, or frequency. Modifying any of these aspects using a message signal allows us to encode data.
2. Message Signal
- The message signal (also called the baseband signal) contains the original information that needs to be transmitted. It is generally a low-frequency signal, such as voice, data, or binary information.
- This signal is combined with the carrier through modulation, which alters the carrier’s characteristics to reflect the message data.
3. Modulation Process
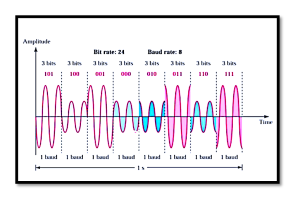
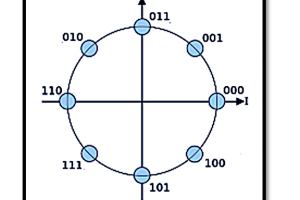
- Modulation involves altering one or more properties of the high-frequency carrier wave in accordance with the lower-frequency message signal. The primary types of modulation are:
- Amplitude Modulation (AM): Changes the amplitude of the carrier based on the message signal.
- Frequency Modulation (FM): Alters the frequency of the carrier to encode the information.
- Phase Modulation (PM): Adjusts the phase of the carrier wave.
- At the output, we obtain a modulated carrier wave, which now contains the information from the message signal.
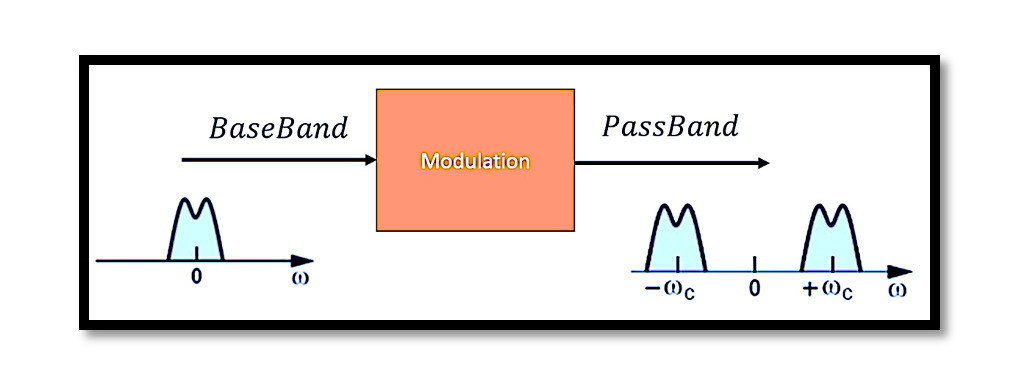
Modulation in Frequency Domains
When modulation occurs, the baseband signal is converted to a passband signal. This shift moves the message signal from its original low-frequency spectrum up to a higher frequency band. This frequency shift is essential for:
- Efficient Transmission: Higher frequencies enable longer-distance communication.
- Frequency Multiplexing: Different signals can share the same medium without interference, as they occupy separate frequency bands.
Frequency Shift and Spectrum
The output of modulation is a passband spectrum, where the modulated carrier wave now occupies a higher frequency band. The modulated signal, once transmitted, can then be received and demodulated to retrieve the original baseband signal.
The Role of the Transmission Channel
After modulation, the modulated carrier wave is transmitted through a channel (air, cable, or fiber). Channels introduce two main challenges:
- Noise: External interference that can distort the signal.
- Attenuation: The signal loses strength as it travels over distance.
To counter these issues, communication systems use error correction and signal amplification methods.
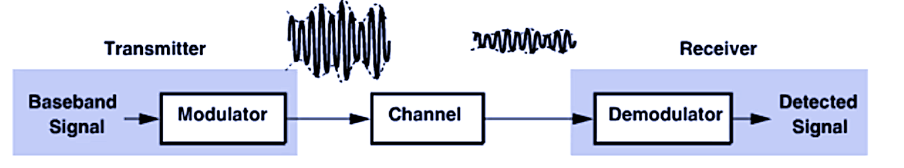
Demodulation: Recovering the Original Signal
The inverse of modulation is demodulation, which is used at the receiver end. This process involves:
- Extracting the message signal: The receiver isolates the original low-frequency baseband signal from the modulated carrier.
- Detecting Data: By demodulating the carrier, the receiver restores the information initially transmitted, whether it’s voice, data, or other types of messages.
Summary: The Modulation and Demodulation System
- Baseband Signal: Initially, we have a low-frequency baseband signal (e.g., voice or binary data).
- Modulation: This baseband signal modulates a high-frequency carrier wave, resulting in a modulated passband signal.
- Transmission through Channel: The modulated signal is sent through a channel, encountering noise and attenuation.
- Demodulation: At the receiver, demodulation retrieves the original baseband signal, enabling data recovery.
Understanding modulation and demodulation is crucial for careers in fields such as telecommunications, radio broadcasting, satellite communication, and data networking. These concepts form the foundation of modern communication technology, allowing us to transmit information reliably across vast distances.

Learn more about this topic by taking the complete course ‘Introduction to Modulation in Communication Systems Online Course – RAHRF152’. Watch the course videos for more detailed understanding. Also checkout other courses on RF system and IC design on https://rahsoft.com/courses/. Rahsoft also provides a certificate on Radio Frequency. All the courses offer step by step approach.