What is Time Division Duplexing (TDD)?
Time Division Duplexing (TDD)
In the previous blog, we discussed about the basic structure of the transceiver and the duplexer block. Duplexer acts as a decision block like a switch between the transmitter and receiver part. There are different types of duplexing, one of them is TDD which is time division duplexing.
TDD uses the same frequency band for bidirectional flow assigning different time slots for uplink and downlink transmission. The information can be voice, data, or video. The time slot can be as long as 1 byte or frames of multiple bytes.
A good example can be a walkie-talkie, which has a button used to talk. Using a single frequency band to both receive and transmit by using different time slots allows both parties to share the same transmission medium. A person can communicate only when the button is pushed and released for the other end person to talk. This button acts as a switch on a walkie-talkie working on TDD, where talking and listening cannot be done at the same time. This toggling operation over a time interval is the basis of TDD operation.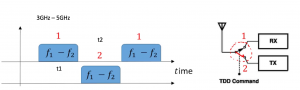
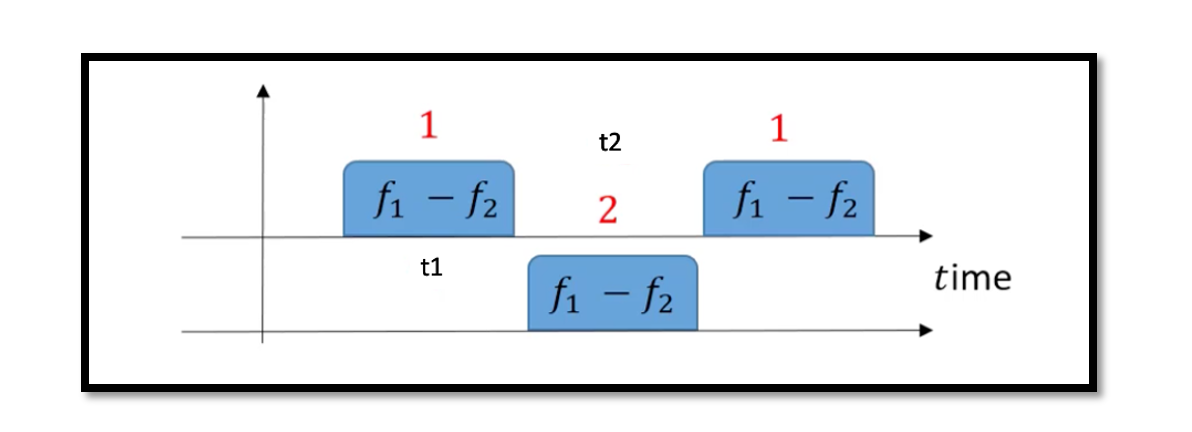
In TDD same frequency band is used for both the transmitter and receiver. We will explain this using the example above. The below figure shows the time axis, and we will be using the TDD method to receive and send data. On the right side, you can see what looks like a switch between Rx and Tx which is the duplexer. At time t1 we are switching Rx, so it means we are only receiving this band 3Ghz to 5GHz for example. So t1 is only for receiving data and is not allowed to send any data. At time t2 we are sending the data where the duplexer switches to Tx, so t2 transmits data and the channel doesn’t change. At one time we are transmitting data and at another time receiving with the same frequency range. In TDD the two tasks are separated, and it depends on time, at one time we are sending data, and at another time we are transmitting but it doesn’t allow both receiving and transmitting at the same time. So in summary the switch is a time domain block that connects the antenna to either Rx or Tx but not at the same time.
Advantages of TDD:
- Cost-effective as it uses the same circuitry for Tx and Rx
- Can be used for uplink and downlink handling a mix of both traffic in separate time slots.
- Use of better frequency spectrum for operation given its narrow banded.
Disadvantages of TDD:
- Needs proper attention to avoid interference between the transmission, hence synchronization is important for uplink and downlink.
- Latency is involved in TDD due to symmetric traffic requirements which can incur a delay.
- Radios closer to the range can cause interference unless concurrent symmetric send and receive take place.