Noise Figure (NF) in RF Systems
What is Noise Figure (NF) in RF Systems?
Noise Figure (NF) is a critical parameter in RF (Radio Frequency) systems that quantifies the impact of noise introduced by components, such as amplifiers, on the overall system’s signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). In other words, NF measures how much additional noise a component adds to the signal as it passes through.
In RF systems, minimizing noise is crucial because it directly affects the quality of received signals. A lower NF indicates better performance, as it means the component adds less noise to the incoming signal.
The Formula for Noise Figure (NF)
The Noise Figure (NF) of an RF component is typically expressed in decibels (dB) and can be calculated using the following formula:
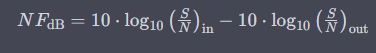
Where:

Example of Noise Figure Calculation
Let’s consider an example to calculate the Noise Figure (NF) of an RF amplifier. Suppose we have an amplifier with the following characteristics:
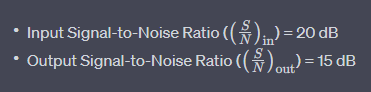
Using the formula for Noise Figure (NF), we can calculate:
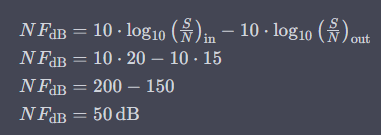
So, the Noise Figure (NF) of the RF amplifier is 50 dB.
Noise Figure Calculation for RF Cascaded System
In RF systems, it’s common to have multiple components cascaded together, each with its Noise Figure. To calculate the cascaded Noise Figure (NF_total) of the entire system, you can use the following formula:

This formula takes into account the gains (G1,G2,G3,…) of the components to calculate the cumulative noise contribution of the entire system.
Let’s illustrate this with an example:
Suppose we have two RF amplifiers cascaded together, each with its Noise Figure and gain:

To calculate the cascaded Noise Figure (NF_total) of the system:

So, the cascaded Noise Figure (NF_total) of the two amplifiers is approximately 3.3 dB. This calculation accounts for the noise contributions and gains of both amplifiers in the cascaded system.
