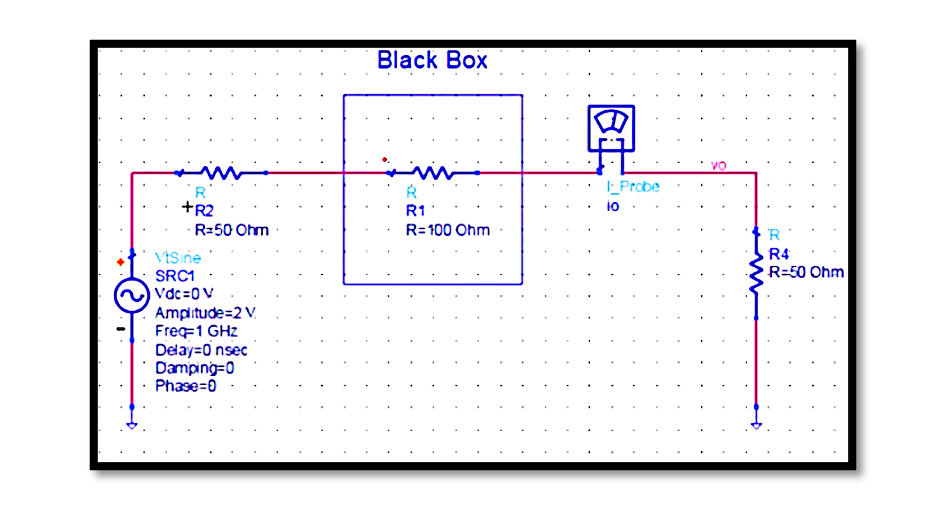
1. Introduction to Available and Transducer Power Gain: Available power gain (GA) and transducer power gain (GT) are essential metrics in the characterization of two-port networks, especially in RF and microwave systems. They quantify the efficiency with which a network …
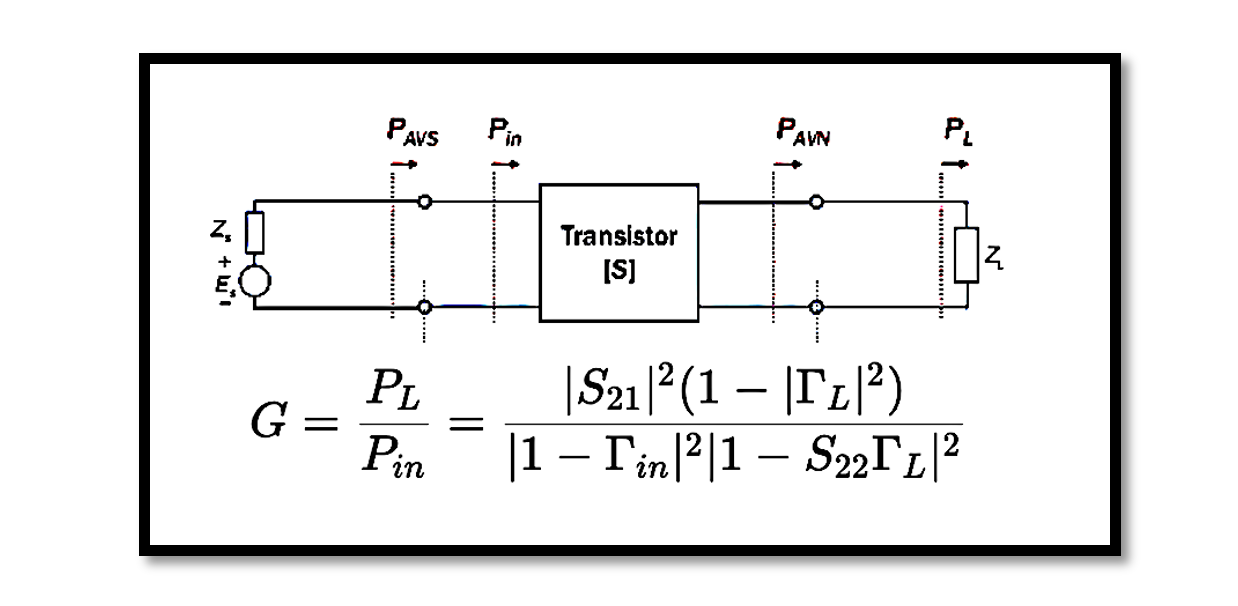
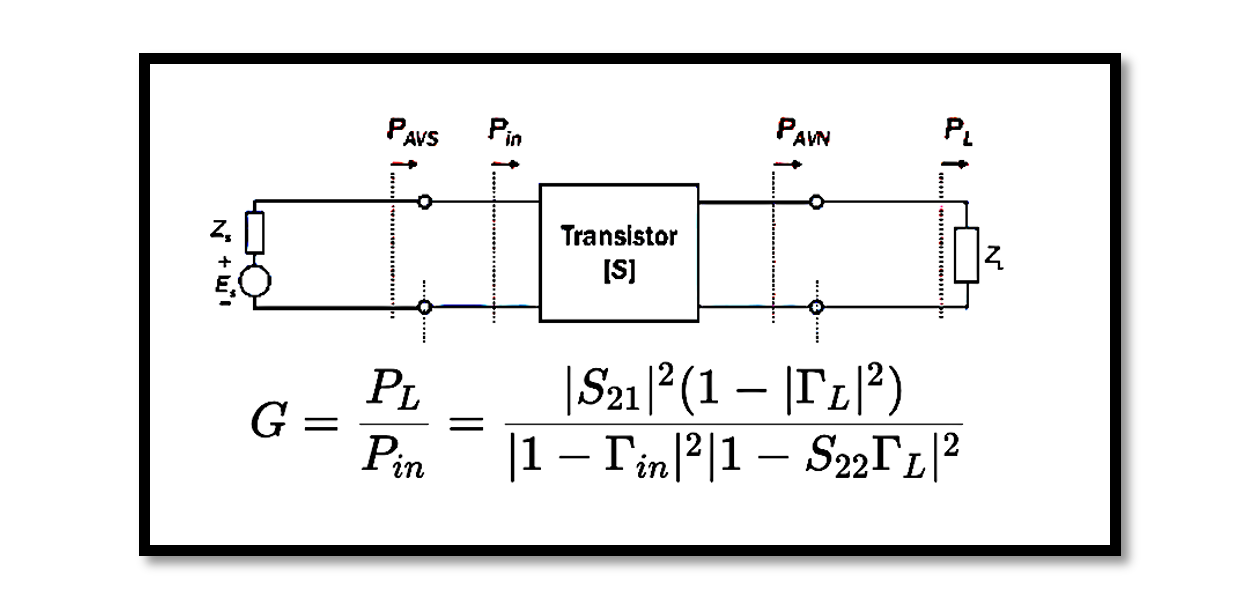
In electronic systems, power gain is a crucial parameter that quantifies the amplification capability of a device or a network. It measures the increase in power between the input and output of a system. Power gain is particularly significant in …
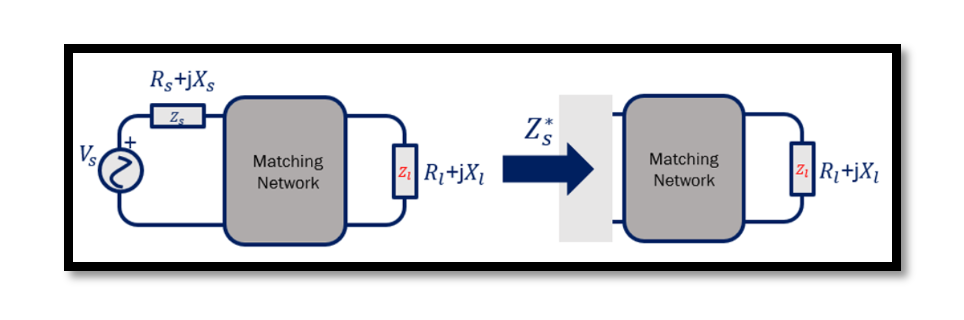
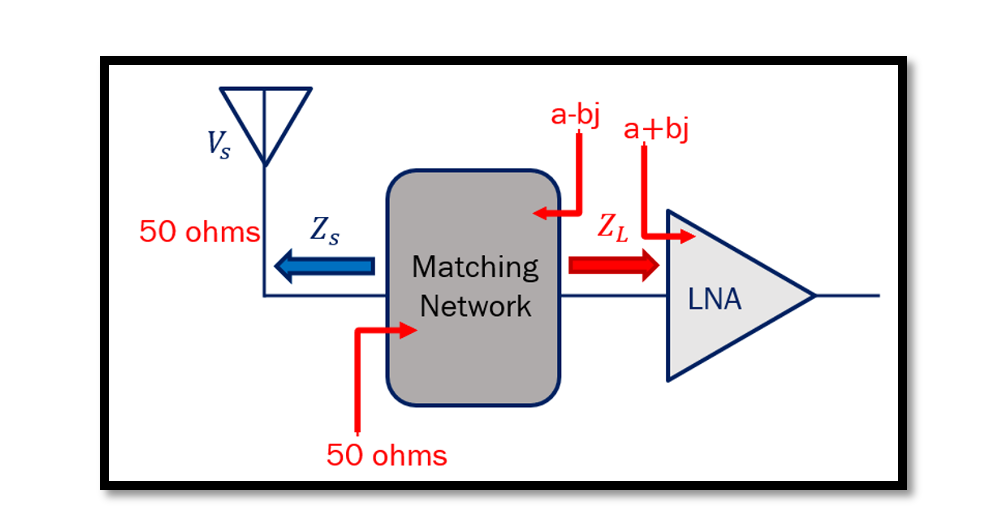
Impedance matching between the antenna and the Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) is crucial for optimizing the performance of RF systems. The inherent impedance of antennas, typically around 50 ohms, needs to be efficiently transferred to the input impedance of the …
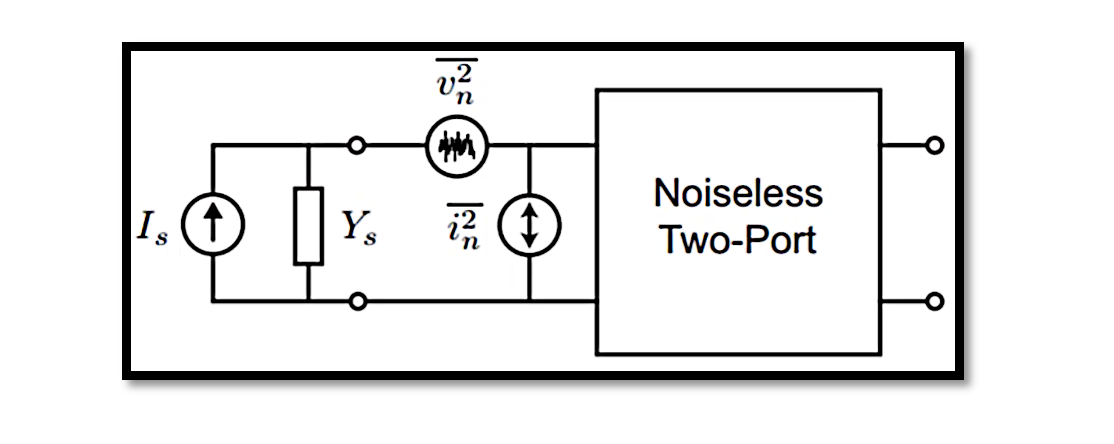
In electronic engineering, understanding noise figure is paramount, especially when it comes to designing communication systems and amplifiers. In a 2-port network, noise figure plays a pivotal role in determining the system’s overall noise performance. Let’s delve deeper into the …
Introduction to Transducer Power Gain Transducer power gain (GT) is a crucial parameter in electrical engineering, particularly in the analysis of signal processing circuits and systems. It quantifies the efficiency with which a transducer, such as a sensor or a …
Amplifier Model Matching Networks play a crucial role in optimizing the performance of amplifiers by ensuring maximum power transfer between different components. In the context of an antenna and Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) setup, impedance matching becomes particularly important. The …
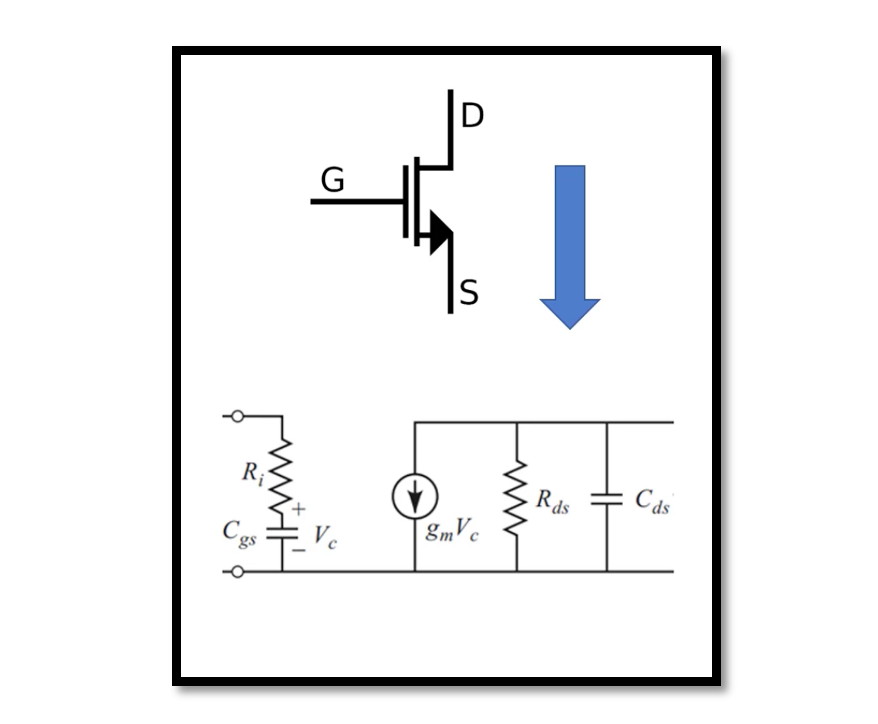
The single-stage transistor, often hailed for its simplicity, plays a pivotal role in the realm of electronics. At its core lies a solitary transistor, typically of the bipolar junction transistor (BJT) variety, accompanied by a handful of passive components like …
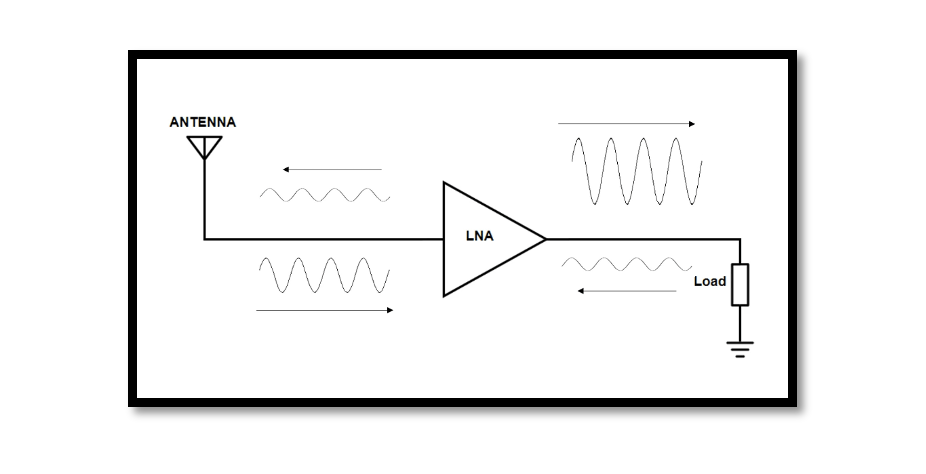
Introduction Low-Noise Amplifiers (LNAs) are critical components in radio frequency (RF) systems, essential for amplifying weak signals while adding minimal noise. Designing an LNA requires careful consideration of various parameters to achieve optimal performance. In this guide, we’ll walk through …
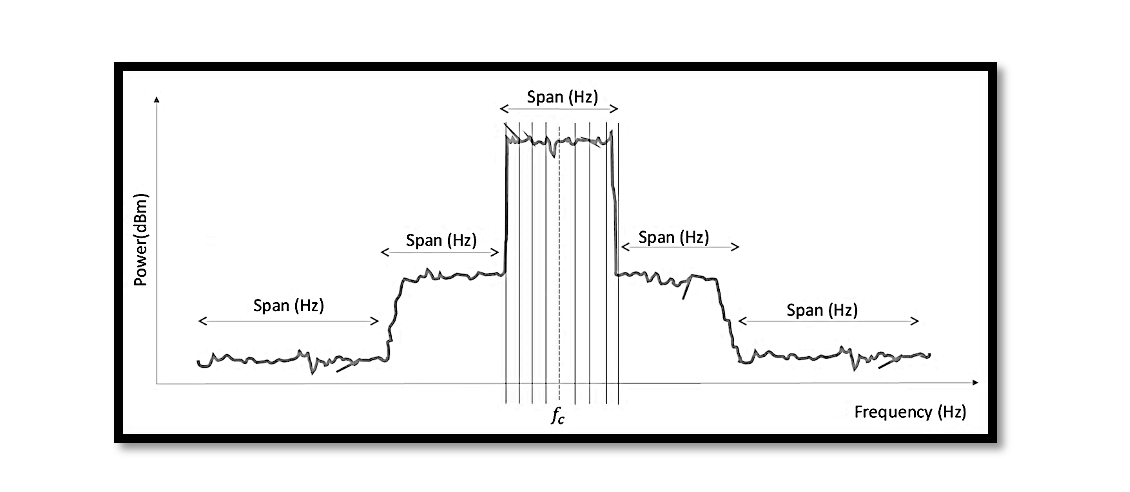
In the complex world of radio frequency (RF) communication, ensuring signal integrity and minimizing interference are paramount. One crucial metric that engineers and technicians rely on is Adjacent Channel Power (ACP). ACP, often referred to as the power level of …
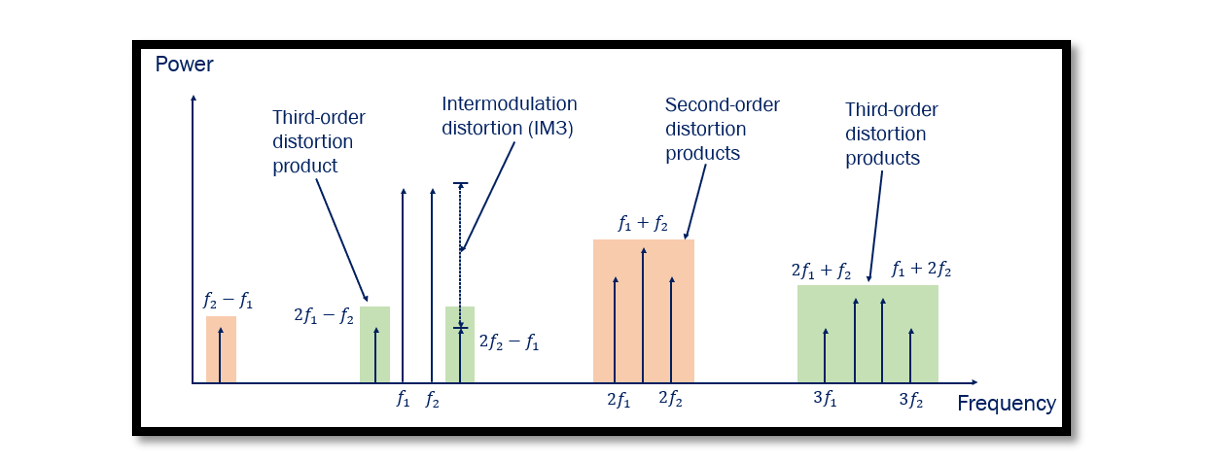
The Third Order Intercept Point, or IP3, serves as a pivotal parameter characterizing the behavior of RF systems. At its core, IP3 delineates the point at which the third-order intermodulation distortion’s power (IMD3) coincides with the extrapolated linear output power …