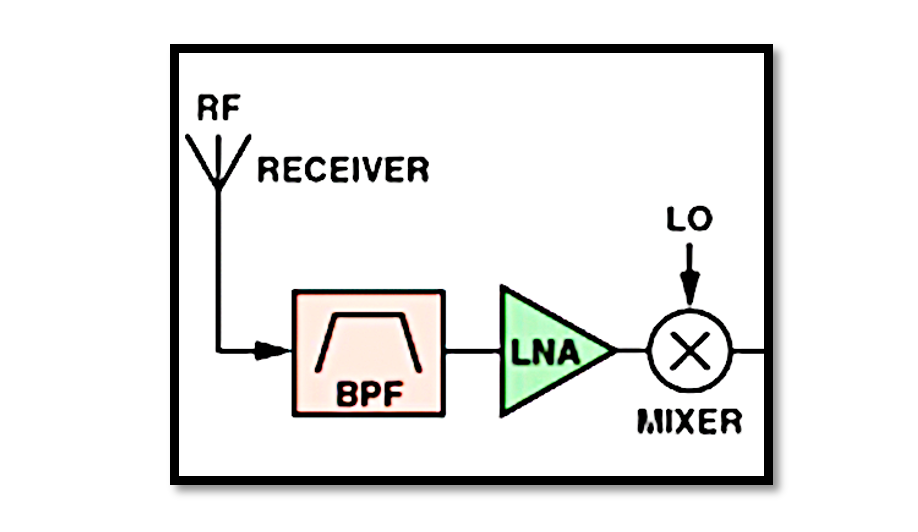
The concept of Noise Figure holds significant importance in the evaluation and optimization of electronic devices such as Low Noise Amplifiers (LNAs), Mixers, and receivers, which play crucial roles in signal processing and communication systems. Ensuring minimal Noise Figure in …
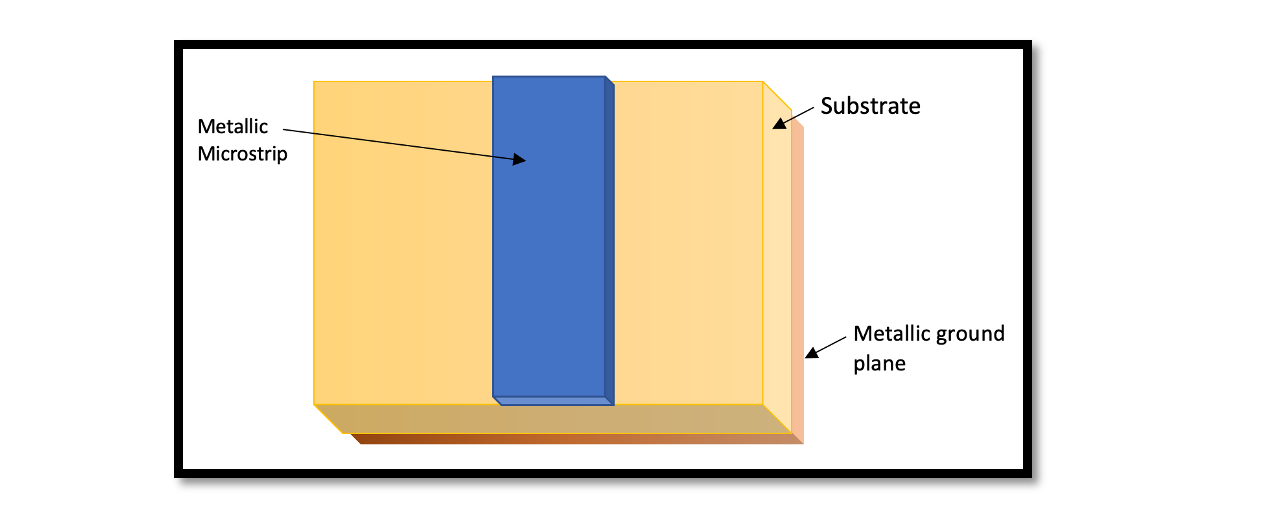
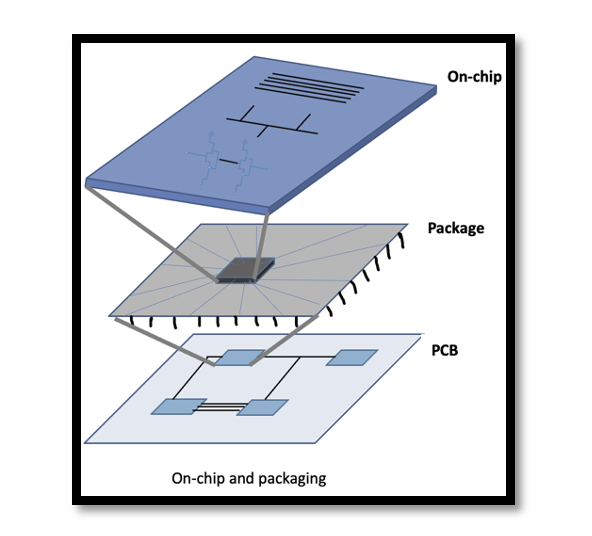
Introduction The design of low noise amplifiers (LNAs) plays a crucial role in various applications such as wireless communication systems, radar systems, and satellite communication. Among the myriad of techniques available, the utilization of microstrip transmission lines stands out as …
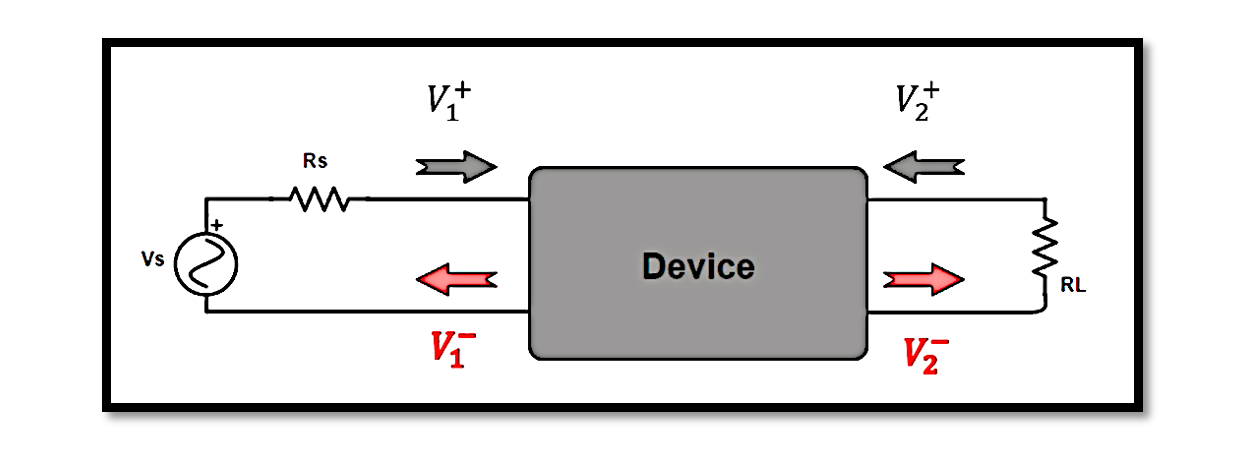
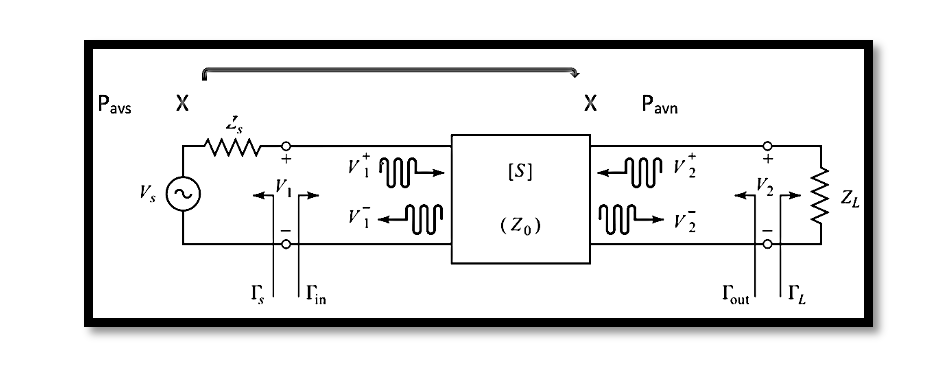
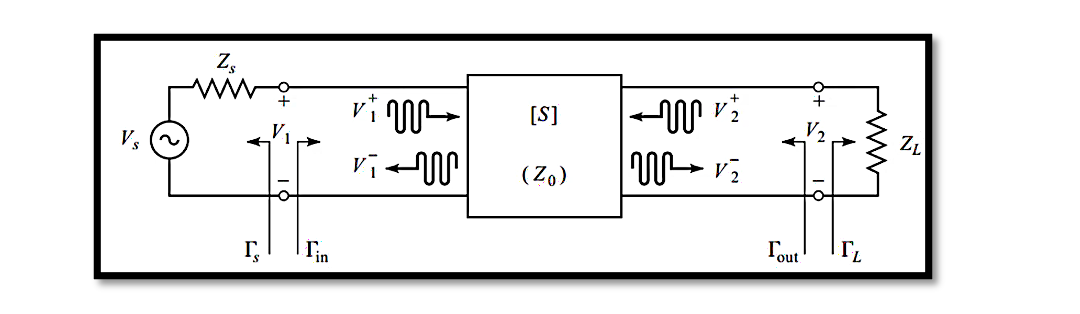
The analysis of two-port networks is fundamental. Whether you’re designing a circuit or troubleshooting an existing one, understanding how signals propagate through these networks is crucial. This is where S-parameters come into play. S-parameters, or scattering parameters, provide a concise …
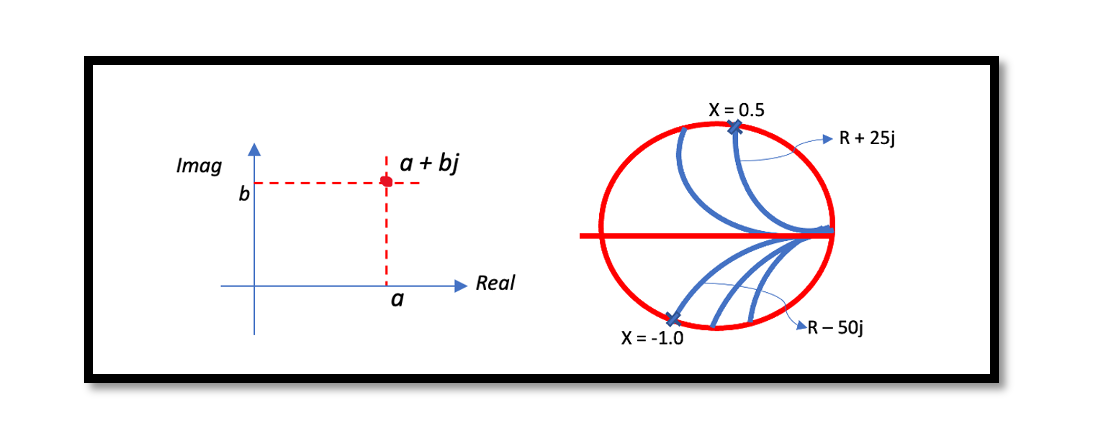
The Smith Chart plays a crucial role in the design and analysis of Microwave Amplifiers and Low-Noise Amplifiers (LNAs) by providing valuable insights into impedance matching, stability analysis, and overall performance optimization. Here’s how Smith Chart concepts are utilized in …
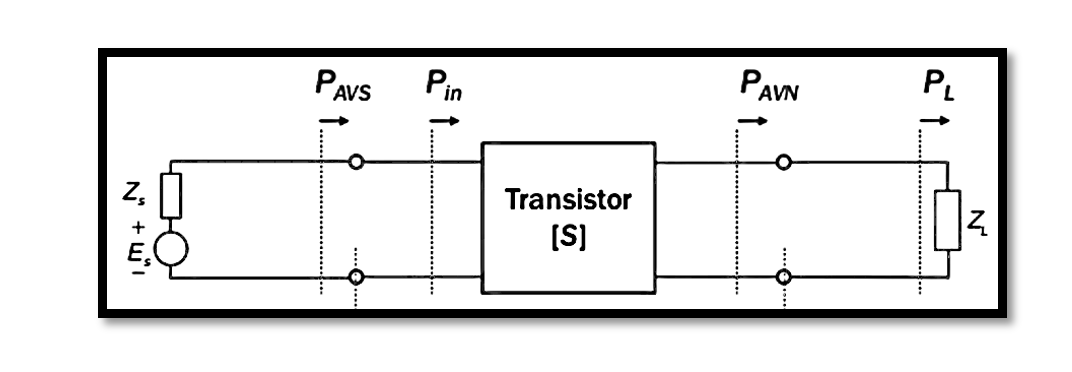
Transducer power gain, denoted as GT, encapsulates the ratio between PL and PAVS, representing the power delivered to the load and the power available at the source, respectively. In simpler terms, it measures how effectively power is transferred from the …
Available power gain, denoted as GA, is a crucial parameter in evaluating the efficiency of power transfer within a network. It’s pivotal to comprehend its equation and significance for optimizing system performance. Equation and Definition The formula for available power …
In two-port networks, the concept of power gain holds significant importance, offering multiple definitions crucial for the design and analysis of amplifiers. These definitions are interrelated, providing a comprehensive framework to optimize amplifier performance. As we delve deeper, we’ll craft …
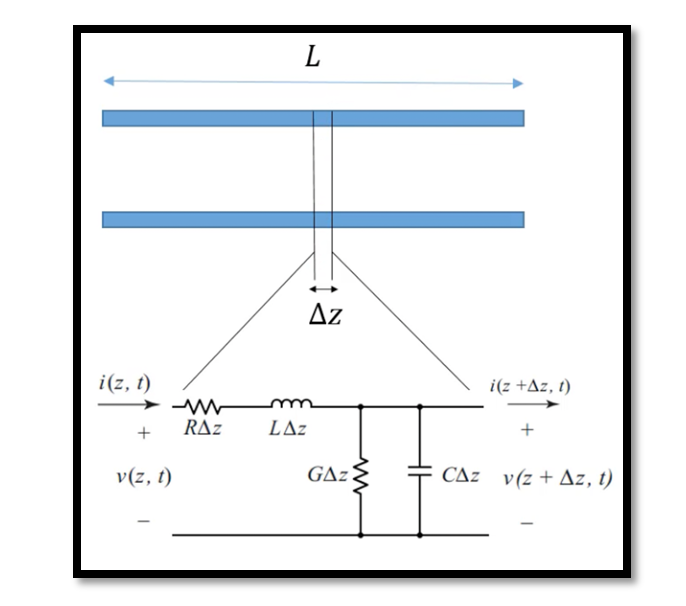
In transmission line analysis, the intricate interplay between voltage and current along its length necessitates a meticulous approach. Consider a transmission line with a length L and select a minute segment ΔZ for examination. This segment, owing to its diminutive …
In distributed analysis, we dive into the intricacies of electrical systems, recognizing that current doesn’t flow uniformly along conductors and elements. Unlike lumped analysis, which simplifies elements as uniform, distributed analysis scrutinizes systems like transmission lines, where such simplifications fall …
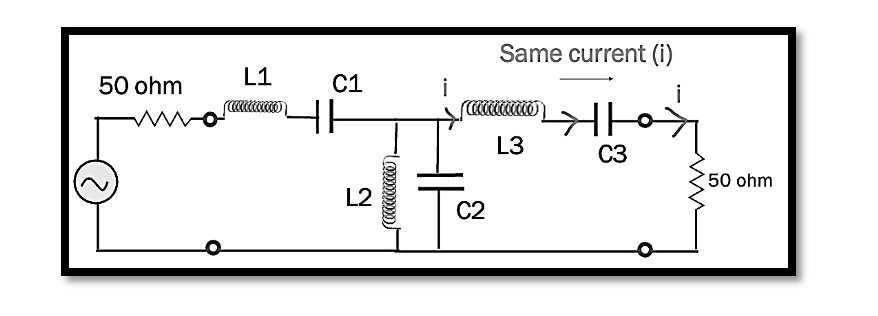
What is Lumped Circuits? Lumped Circuit Analysis represents a foundational approach in the field of electronic circuit design, premised on the Lumped Element Model. This model simplifies the complex reality of electronic circuits by assuming that key characteristics such as …