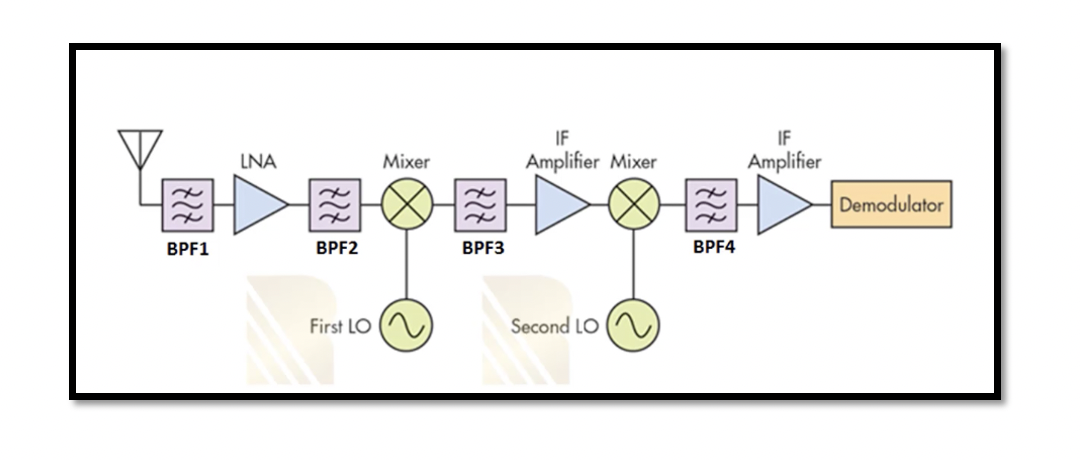
Dual Conversion As discussed in the previous section, ‘Image Rejection vs Channel Selection’, there is a constant trade-off between the two. There is efficient filtering in low wIF, but the image rejection is insufficient, and in high wIF, the Image …
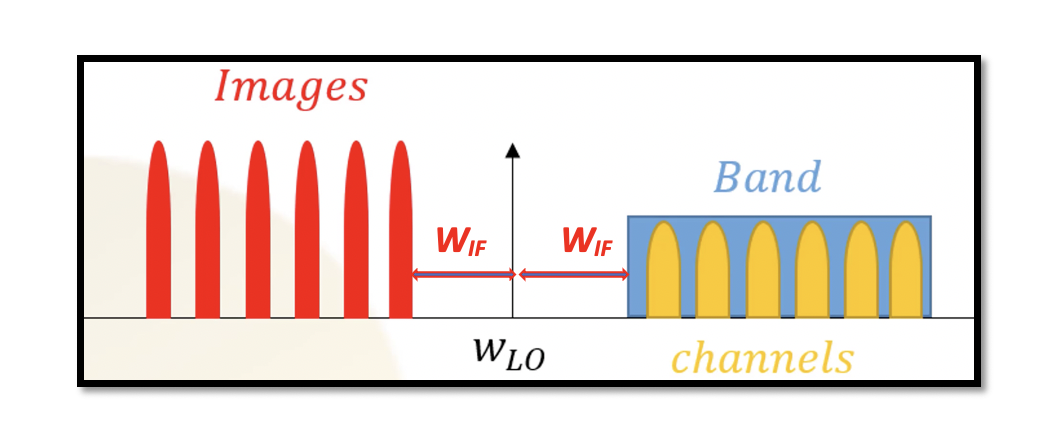
Understanding the trade-off in choice of IF There is a trade-off between image rejection and channel selection receiver. So there are two options in selecting the frequency of the local oscillator, or carrier says we have two options in choosing …
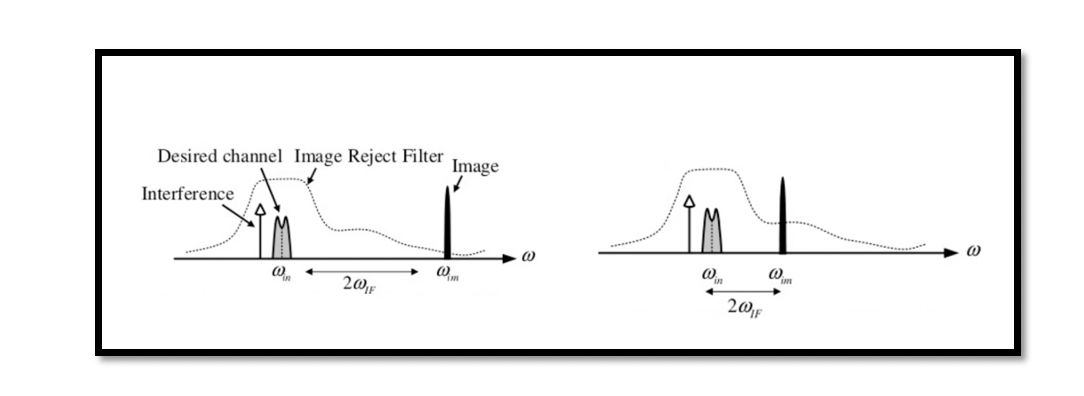
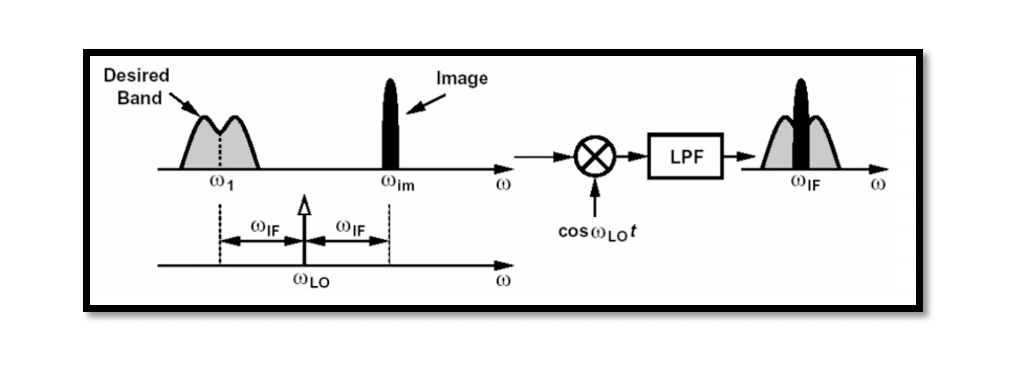
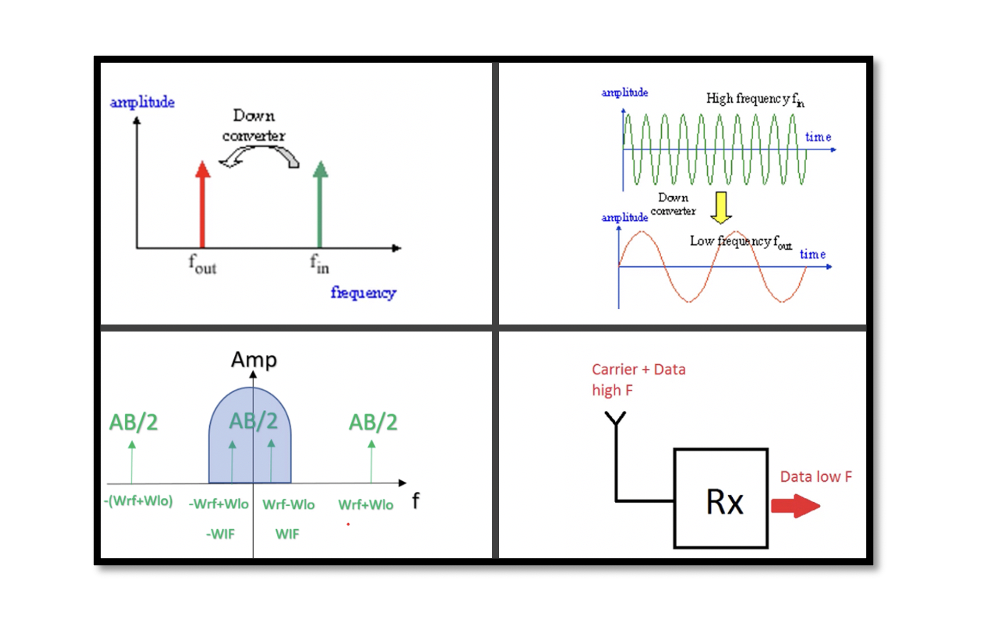
As discussed in the section ‘Image problem in the heterodyne receiver’, that image signal’s frequency is quite close to the desired band, but it is outside the band. So to remove the image signal from the desired channel, a filter …
High-side injection: We have a channel, and to do down conversion, this channel is mixed with a local oscillator. There are two options to do this: first, we choose the frequency of the local oscillator (wLO) above the desired channel; …
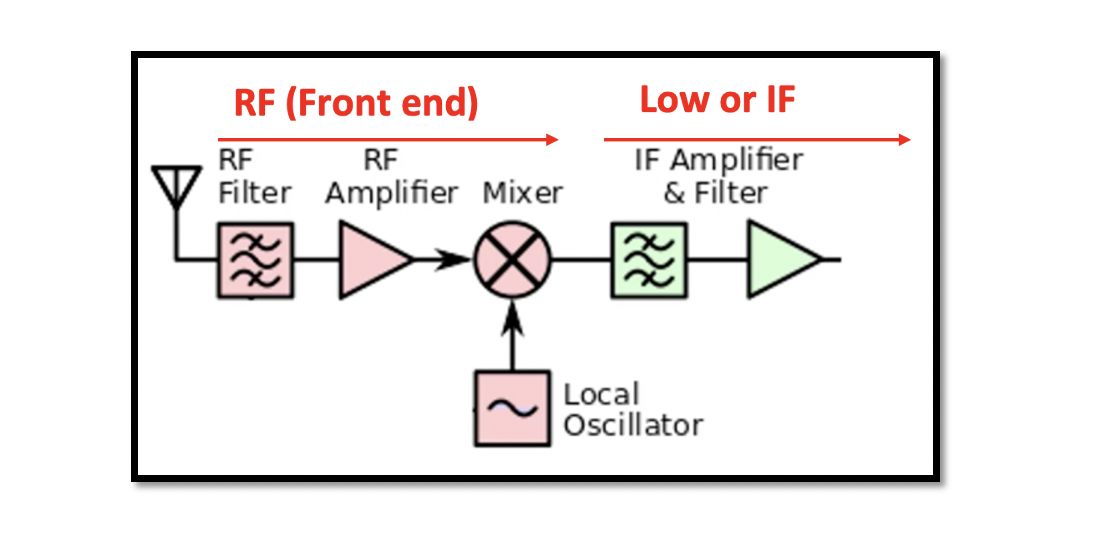
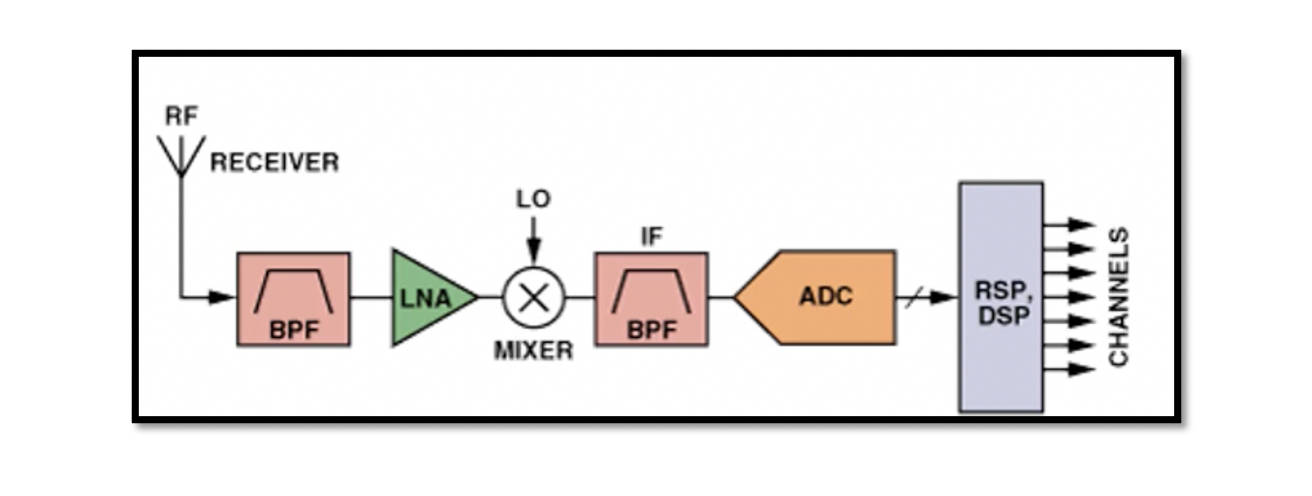
Heterodyne Receiver In a heterodyne receiver the received signal from an antenna is down converted from RF signal to intermediate frequency. Win is not equal to WLO. The basic structure of heterodyne receiver is shown below. There is an antenna …
Down Conversion Down conversion occurs in the receiver. Before transmitting the data, it is shifted to high frequency and is captured by the antenna and passed on to the receiver. The captured signal is then shifted from high frequency to …
An RF module is a block that has sub-blocks inside it. It is a small electronic circuit used to transmit and receive radio waves on one of a number of carrier frequencies. These carrier waves have high frequencies. RF module …
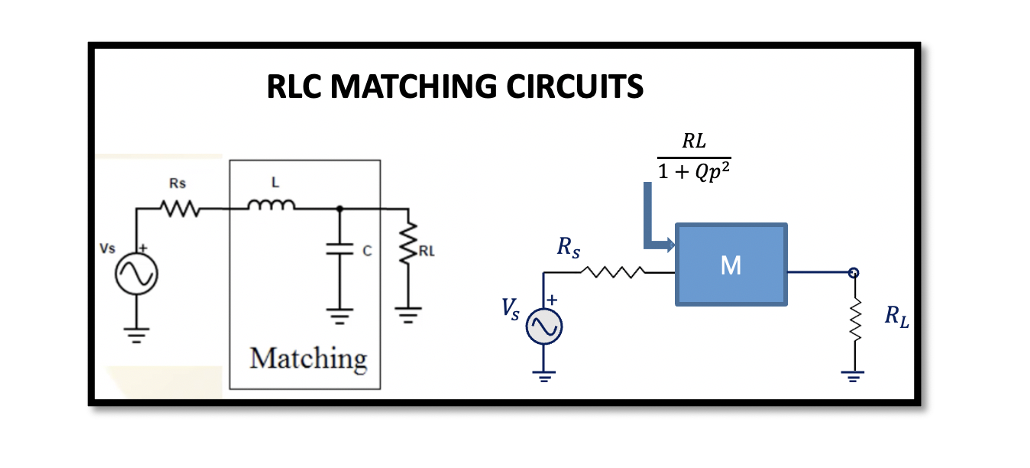
Why matching circuits are needed? As we know that in RF systems maximum power delivery is the main objective while designing a circuit and to maximise the power delivery with minimum loss, matching networks are created. Read understanding the need …
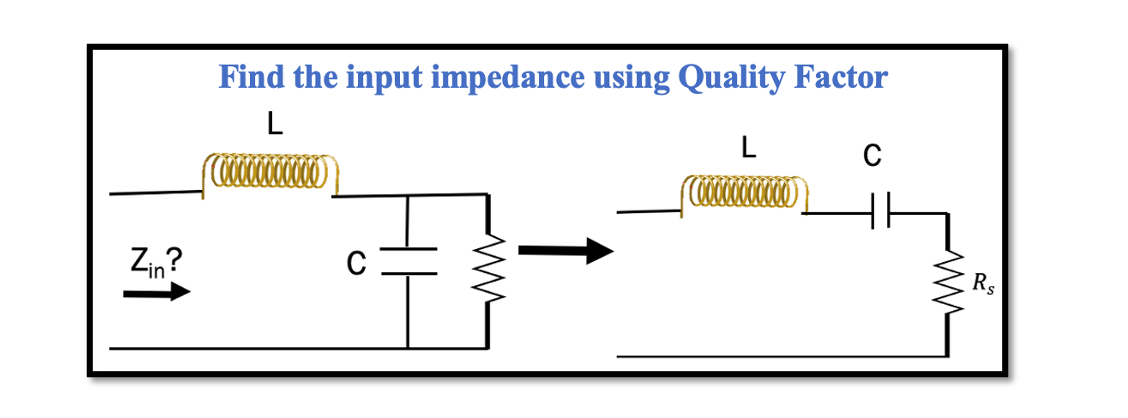
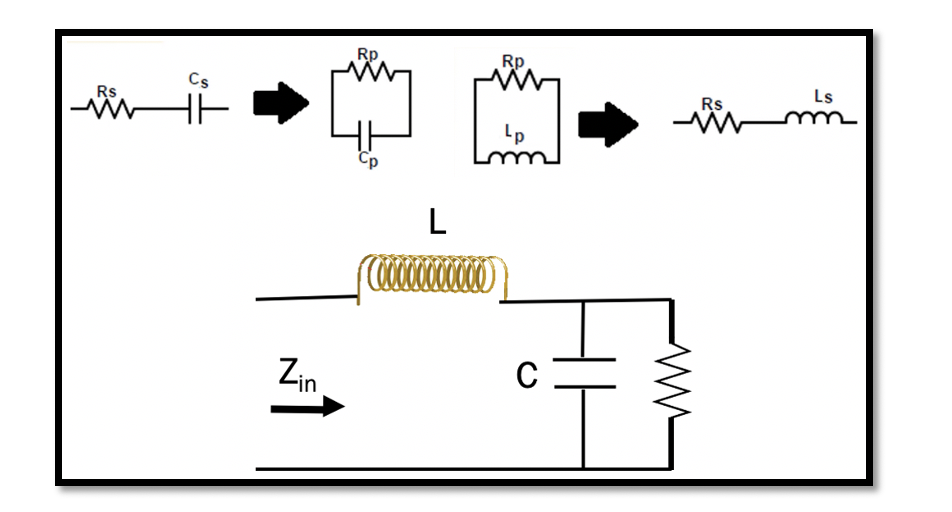
In the previous section, Resonance and Quality Factor we discussed the method 1 for series to parallel conversion and vice versa using Quality factor. To give a summary of method 1, this method is a process of conversion of series …
Resonance: Resonance in a RLC circuit is when we cancel out all the reactants in the circuit. In RLC circuit L & C are the reactants. So the reactances of inductance and capacitance are essentially cancelled out, and only resistance …