Course Title: RF Microwave and Radio Frequency Transmission Theory Online Course – RAHRF200
Course Description:
Are you ready to delve into the fascinating world of RF Microwaves and Radio Frequency Transmission Theory? Welcome to RAHRF200, a comprehensive online course designed to equip you with a complete understanding of RF Microwaves, Transmission Line Theory, Smith Chart, and Impedance Matching. Whether you’re an electrical engineer, communication engineer, RF engineer, antenna engineer, hardware engineer, electrical engineering student, or simply an RF enthusiast, this course is your gateway to mastering these essential concepts.
What You’ll Learn:
- Transmission Line Theory: Explore the fundamentals, including distributed versus lumped analysis, phasor equations, characteristic impedance, lossless transmission lines, time domain equations, wave propagation, standing waves, and more.
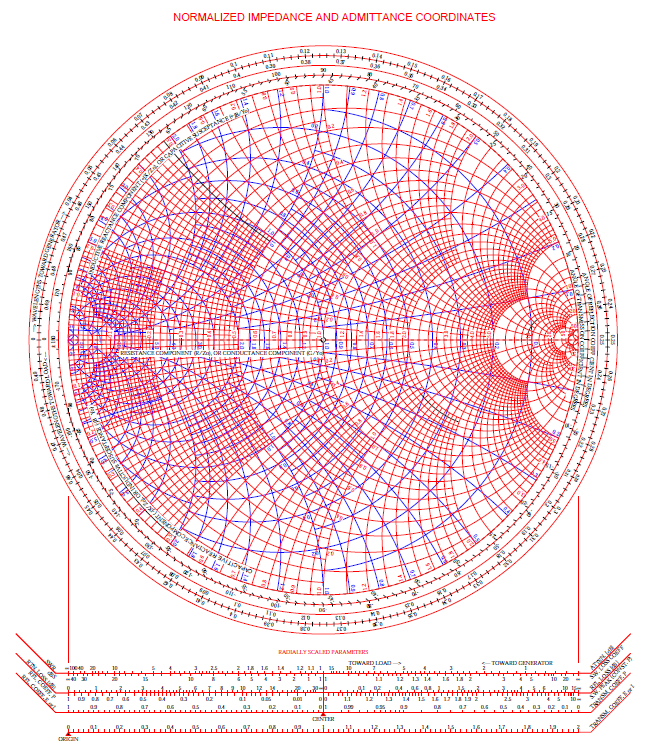
- Smith Chart: Gain insights into the Smith Chart, its impedance representation, reflection coefficient, Z to Y conversion, and practical applications. Experience Smith Chart analysis using ADS simulation.
- Impedance Matching: Learn about impedance matching, both with lumped components and transmission lines. Explore single stub tuning, complex load to complex source impedance matching, wideband matching, and microstrip lines. Practice impedance matching through ADS simulations.
Requirements:
- Solid understanding of calculus.
- Familiarity with basic electrical engineering concepts.
- While RAHRF101 and RAHRF152 prior courses are preferred for a deeper foundation, they are not mandatory.
Course Prerequisites:
RAHRF200 is the third course in the Rahsoft RF Certificate program. While it is recommended to take the courses in order, it’s not mandatory. This course will provide you with valuable knowledge in RF microwaves and transmission theory.
Course Curriculum:
Transmission Line Theory:
- Distributed versus Lumped Analysis
- Transmission Lines
- Phasor Equations
- Characteristic Impedance
- Lossless Transmission Line
- Time Domain Equations
- Wave Propagation and Standing Waves
- Examples and Special Cases
- Quarter Wave Transmission Line
- Bounce Diagrams
Smith Chart:
- Introduction to Smith Chart
- Smith Chart Impedance Example
- Reflection Coefficient Example
- Z to Y Conversion
- Smith Chart and Transmission Lines Example
- Smith Chart and Transmission Lines ADS Simulation
- Quarter Wave TL on Smith Chart
Impedance Matching:
- Impedance Matching Introduction
- Impedance Matching with Lumped Components
- Complete Version of Smith Chart
- Impedance Matching with Lumped Components ADS Simulation
- Impedance Matching with Transmission Lines – Single Stub Tuning
- Single Stub Tuning Example
- Single Stub Tuning Example ADS Simulation
- Matching with Quarter Wave TL Example
- Complex Load to Complex Source Impedance Matching
- Complex to Complex Impedance Matching – ADS Simulation
- Wide Band Matching with Constant Q Lines on Smith Chart
- Wide Band Matching Circuit Design in ADS
- Wide Band Matching Circuit Design using Impedance Matching Tool
- Wide Band Matching Using Transmission Lines
Microstrip Line and EM Simulation:
- Microstrip Lines
- Microstrip Lines Calculation Example
- Defining Substrate in ADS
- Design of Matching Circuit using Microstrips
This course is a stepping stone for electrical engineers, communication engineers, RF engineers, antenna engineers, hardware engineers, electrical engineering students, and RF enthusiasts to deepen their knowledge of RF Microwaves and Transmission Theory.
Course Features
- Lectures 42
- Quiz 0
- Duration 7 hours
- Skill level All levels
- Language English
- Students 1764
- Certificate Yes
- Assessments Yes
Curriculum
- 4 Sections
- 42 Lessons
- 900 Weeks
- Transmission line theory17
- 2.1RAHRF200 Before We Start
- 2.28.1.1.1 Distributed versus Lumped Analysis12 Minutes
- 2.38.1.1.2 Transmission Lines6 Minutes
- 2.48.1.1.3 phasor equations12 Minutes
- 2.58.1.1.4 characteristic impedance8 Minutes
- 2.68.1.1.5 Lossless Transmission Line11 Minutes
- 2.78.1.1.6 Time Domain Equations16 Minutes
- 2.88.1.1.7 Wave Propagation and standing waves8 Minutes
- 2.98.1.1.8 Example10 Minutes
- 2.108.1.2.1 Terminated Transmission Line16 Minutes
- 2.118.1.2.2 Terminated Transmission Line Example13 Minutes
- 2.128.1.2.3 Vmax and Vmin11 Minutes
- 2.138.1.2.4 Special Cases of Lossless Terminated Lines11 Minutes
- 2.148.1.2.5 Special Cases of Lossless Terminated Lines Example8 Minutes
- 2.158.1.2.6 Quarter Wave Transmission line12 Minutes
- 2.168.1.2.7 Quarter Wave Transmission line Example9 Minutes
- 2.178.1.3.1 Bounce Diagrams26 Minutes
- smithchart7
- 3.18.2.1.1 Introduction to Smith Chart23 Minutes
- 3.28.2.1.2 Smith Chart Impedance example4 Minutes
- 3.38.2.1.3 Reflection Coefficient Example5 Minutes
- 3.48.2.1.4 Z to Y conversion6 Minutes
- 3.58.2.2.1 Smith Chart and Transmission lines Example20 Minutes
- 3.68.2.2.2 Smith Chart and Transmission lines ADS Simulation16 Minutes
- 3.78.2.2.3 Quarter wave TL on smith chart7 Minutes
- Impedance matching14
- 4.18.3.1.1 Impedance Matching Introduction10 Minutes
- 4.28.3.1.2 Impedance Matching with Lumped components5 Minutes
- 4.38.3.1.3 Complete version of Smith Chart13 Minutes
- 4.48.3.1.4 Impedance Matching with Lumped components ADS Simulation6 Minutes
- 4.58.3.2.1 Impedance Matching with Transmission lines – Single Stub Tuning8 Minutes
- 4.68.3.2.2 Single Stub Tuning Example13 Minutes
- 4.78.3.2.3 Single Stub Tuning Example ADS Simulation6 Minutes
- 4.88.3.2.4 Matching with Quarter Wave TL Example6 Minutes
- 4.98.3.2.5 Complex load to Complex Source Impedance Matching8 Minutes
- 4.108.3.2.6 Complex to Complex Impedance Matching – ADS Simulation4 Minutes
- 4.118.3.3.1 Wide Band Matching Constant Q lines on Smith Chart7 Minutes
- 4.128.3.3.2 Wide Band Matching Circuit Design in ADS11 Minutes
- 4.138.3.3.3 Wide Band Matching Circuit Design using Impedance Matching tool12 Minutes
- 4.148.3.3.4 Wide Band Matching Using transmission lines11 Minutes
- Micro strip line and EM simulation4