Understanding Modulation: The Key to Efficient Communication
In the world of telecommunications, modulation plays a fundamental role in how we transmit and receive information over vast distances. Whether it’s making a phone call, listening to the radio, or browsing the internet, the process of modulation ensures that our messages can travel from one point to another effectively. But what exactly is modulation, and why is it so essential?
Why Do We Need Modulation?
At its core, modulation is the process of embedding a message signal, such as a digital bit stream or an analog audio signal, into another signal that can be physically transmitted. This other signal, often referred to as the “carrier,” serves as the vessel for transporting the message through a medium such as air, cables, or optical fibers. One way to think of modulation is like sending a letter in an envelope. The letter represents your message, while the envelope is the carrier that ensures your message reaches its destination. Without the envelope, the letter (or message) wouldn’t be able to travel safely through the postal system (the transmission medium). Similarly, in telecommunications, modulation allows us to “package” our data for smooth transmission across communication channels.
The Role of the Carrier Signal
The carrier signal plays a critical role in the modulation process. It is usually a high-frequency signal that can carry the message data over long distances or through various mediums. By modulating the carrier with the message data, we ensure that the signal is optimized for transmission. This modulated signal can then travel through the physical environment, which is commonly referred to as the “channel.” In radio communications, for example, modulation is needed to transmit messages over the available high-frequency radio channels. Since our message signals (like voice or data) often exist in lower frequencies, we cannot directly send them over long distances. Instead, modulation “shifts” these lower-frequency messages onto a higher-frequency carrier that can propagate efficiently through the air.
Understanding the Transmission Channel
The “channel” in a communication system refers to the environment through which the signal travels. This could be the air, a fiber-optic cable, or even space, depending on the type of communication. When we talk about channels in a phone call, for instance, the channel is essentially the space or area between two phones where the signal moves. Different channels have varying characteristics, such as bandwidth, noise levels, and interference, which can impact the quality of the transmitted signal. Modulation helps overcome these challenges by adapting the message signal to suit the specific properties of the channel, ensuring a reliable transmission.
Adapting Modulation to Channel Characteristics
One of the key reasons we need modulation is to ensure that the signal is optimized for the transmission channel. Different channels come with different challenges — such as noise, interference, or limited bandwidth — that can distort the signal or reduce its quality. Therefore, the choice of modulation type must be suited to the specific characteristics of the channel. For example, in noisy environments, we should choose a modulation technique that is less susceptible to noise.
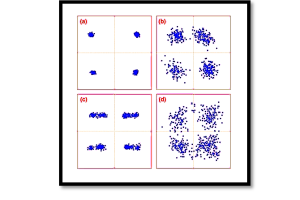
Let’s consider a noisy transmission channel. If the signal is to travel through an environment filled with interference or other signals, we need to choose a modulation method that can handle this noise. Modulation types like Frequency Modulation (FM) or Phase Shift Keying (PSK) are examples of methods that can be used to maintain signal quality even in noisy conditions. By carefully selecting the modulation method, we can minimize the effects of noise and ensure that the message is transmitted clearly.
Shifting Frequencies for Better Transmission
Another critical aspect of modulation is shifting the frequency of the message data to higher frequencies. This is important because lower-frequency signals, such as those produced by human speech or digital data, cannot travel efficiently over long distances or through various types of media. By modulating the data onto a higher-frequency carrier, we make it possible for the signal to propagate more effectively.
Higher frequency signals have a better ability to travel long distances and are less prone to interference, making them ideal for communication purposes. For instance, in radio broadcasting, the audio signal (which is a low-frequency signal) is modulated onto a high-frequency radio wave, allowing it to travel vast distances and be received clearly by radios. Modulation essentially “transforms” the message signal so that it can efficiently pass through the transmission channel and reach the receiver with minimal distortion or loss of quality.
Take our entry level course (Below) for free using coupon code RAHRF101BLOG
RF Fundamentals, Basic Concepts and Components – RAHRF101
For limited time take an additional 10% off of all our courses using coupon code RFCERT10
Rahsoft RF Certificate and courses
Conclusion
In summary, modulation is a vital process in telecommunications, enabling the effective transmission of signals through various types of communication channels. By embedding message signals into carrier waves, we can overcome the limitations of the transmission channel, reduce the impact of noise, and extend the reach of our communication. Whether it’s radio, phone calls, or internet data, modulation ensures that our messages are delivered reliably and with clarity.

Learn more about this topic by taking the complete course ‘Introduction to Modulation in Communication Systems Online Course – RAHRF152’. Watch the course videos for more detailed understanding. Also checkout other courses on RF system and IC design on https://rahsoft.com/courses/. Rahsoft also provides a certificate on Radio Frequency. All the courses offer step by step approach.