The importance of modulation in Communication Systems
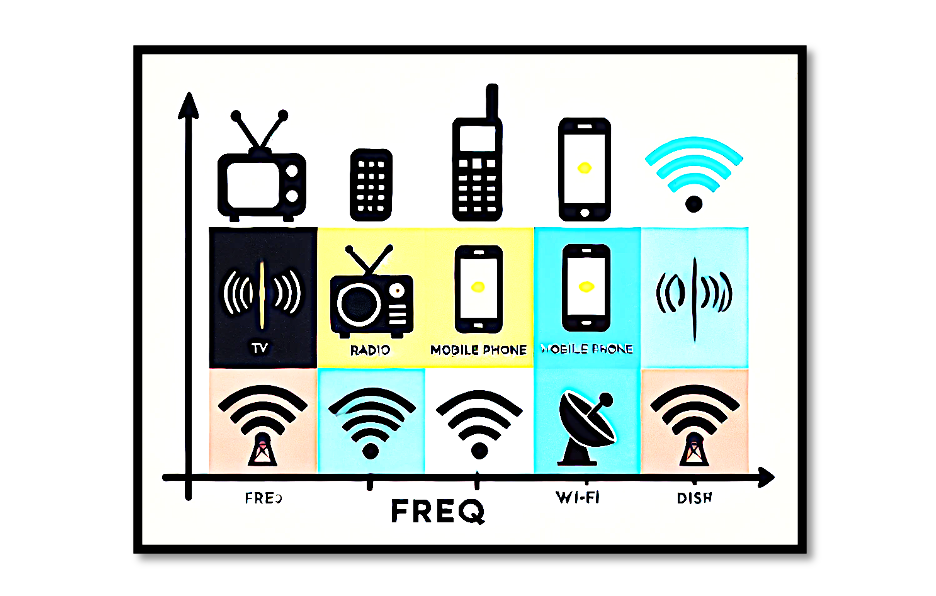
In today’s world communication is everywhere, from mobile phones and radios to TV broadcasts. But have we ever wondered what enables these devices to transmit signals clearly without interference? The key lies in a process called modulation. Modulation plays a critical role in ensuring that signals from mtltiple sources can coexist and reach their intended destinations without chaos.. In this blog we will explore why modulation is essential and how it works.
Why Do We Use Modulation?
At the heart of any communication system is the transfer of signals, whether it’s a phone conversation, a radio broadcast, or a TV transmission. These signals start at low frequencies, and if they were all transmitted as they are, they would interfere with one another. Imagine being in a room with ten people all talking at once—it would be nearly impossible to understand anyone.
This scenario is similar to what happens when multiple devices transmit low-frequency signals simultaneously; they overlap, causing interference. The solution? We use modulation to “shift” each signal to a higher frequency. By doing so, we separate the signals in the frequency domain, ensuring they can be transmitted at the same time without interference.
What is Modulation?
Also, refer to the previous blog on Understanding modulation: the key to efficient communication
Modulation is the process of taking a baseband signal. We shift and altering it so that it can be transmitted over a different frequency. Think of it as transmitted iver a different frequency, Modulation is the process. Modulation is the process that can be transmitted over to a low-frequency range to higher frequency.
Modulation is the process of taking a baseband signal (the original message) and altering it so that it can be transmitted over a different frequency. We “shift” these signals from the low-frequency range to higher frequencies, making it possible to transmit them simultaneously while keeping them distinct. Think of it like tuning into a radio station. Each station broadcasts at a different frequency, allowing you to pick up only one channel at a time, even though many stations are broadcasting simultaneously. Modulation helps us separate those stations in terms of frequency so that each one occupies a unique space on the frequency spectrum.
Benefits of Modulation
Now, let’s look at why modulation is essential in communication systems:
1. Interference Avoidance
Modulation allows different signals to be transmitted without overlapping. By shifting signals to different frequencies, they can all coexist in the same time frame without interfering with each other. This is crucial in our RF (radio frequency) world, which is densely packed with signals from various devices and services. For example, FM radio stations occupy different frequencies—100.1 MHz, 102.5 MHz, etc.—so they don’t interfere with each other, even though they are all broadcasting simultaneously.
2. Efficient Use of the Frequency Spectrum
The frequency spectrum is a limited resource, so making the best use of it is critical. Modulation allows us to transmit multiple signals within the same channel or band by assigning each signal its own frequency. This enables efficient use of bandwidth while preventing overcrowding of signals in a specific range.
3. Better Signal Propagation
Higher frequency signals travel more efficiently over long distances. If we tried to transmit low-frequency signals, they would face significant challenges, such as attenuation (loss of signal strength) and susceptibility to noise. By modulating the signals to a higher frequency, they become more robust and can propagate better, ensuring clearer communication.
4. Smaller Antenna Size
The size of an antenna is directly related to the wavelength of the signal it’s transmitting or receiving. Low-frequency signals have long wavelengths, which would require impractically large antennas. By shifting to higher frequencies, we can significantly reduce the size of the antenna. This is particularly important in mobile phones, radios, and other portable devices where size is a crucial factor.
5. Immunity to Noise
High-frequency signals are less susceptible to certain types of noise and interference. Modulating a signal to a higher frequency makes it more resistant to noise, resulting in clearer reception. This is one of the reasons why modulation is used in digital communication systems, where reliability and clarity are paramount.
6. Multiple Users Can Transmit Simultaneously Another major advantage of modulation is that it allows multiple users to share the same communication channel. Imagine a mobile network with millions of users—without modulation, it would be impossible for all those signals to transmit without chaos. Modulation ensures that each user’s data is assigned to a distinct frequency, allowing for simultaneous transmission without interference.
A Real-World Example: Radio Broadcasting
Radio broadcasting offers a perfect example of how modulation works in practice. Think about how you can switch between different FM stations, each broadcasting music, news, or talk shows. All of these stations transmit their signals over the air at the same time. Thanks to modulation, each station uses a specific frequency (e.g., 100.1 MHz or 102.5 MHz), which allows your radio to tune into one station at a time without mixing the signals from other stations.
Without modulation, all stations would be sending their signals at the same frequency, causing a chaotic blend of sounds—similar to several people talking to you at once. Modulation organizes this mess by assigning each station a unique frequency range.
Key Takeaways in Modulation
Modulation is indispensable for modern communication systems. It provides several advantages, including:
- Interference-free transmission: Signals from multiple sources can be sent simultaneously without overlap.
- Efficient spectrum usage: Multiple signals can coexist in the same frequency range without interfering.
- Smaller antennas: Higher frequency signals require smaller antennas, which is essential for portable devices.
- Better propagation: High-frequency signals travel farther and more efficiently.
- Improved noise resistance: Modulated signals are more resistant to interference.
In conclusion, modulation is the cornerstone of communication systems, enabling us to efficiently and clearly transmit data across the densely packed radio frequency spectrum. Whether it’s ensuring that your mobile call doesn’t interfere with a radio broadcast or that thousands of users can access the internet simultaneously, modulation makes it all possible.
Take our entry level course (Below) for free using coupon code RAHRF101BLOG
RF Fundamentals, Basic Concepts and Components – RAHRF101
For limited time take an additional 10% off of all our courses using coupon code RFCERT10
Rahsoft RF Certificate and courses

Learn more about this topic by taking the complete course ‘Introduction to Modulation in Communication Systems Online Course – RAHRF152’. Watch the course videos for more detailed understanding. Also checkout other courses on RF system and IC design on https://rahsoft.com/courses/. Rahsoft also provides a certificate on Radio Frequency. All the courses offer step by step approach.
Tag:Frequency, Modulation