Understanding Signal Distortion in Communication Systems
In digital communication systems, the accurate transmission of data from sender to receiver is critical. However, the signal often undergoes distortion as it propagates through the channel. This blog explores the mechanisms of signal distortion, focusing on the challenges of pulse shaping, inter-symbol interference, and their effects on data errors.
How Does Signal Distortion Occur?
Signal distortion happens due to the limitations of the communication channel, which typically acts as a low-pass filter. This filtering effect alters the shape of the transmitted pulses, leading to the following issues:
Pulse Shaping and Broadening
- Input and Output Signal Comparison: As depicted in the first slide, the transmitted signal starts as a rectangular pulse representing binary data (e.g., ‘1’ or ‘0’). However, at the channel output, the signal transforms into a smooth, broadened waveform.
- Cause of Broadening: The distortion arises because real-world communication channels cannot support infinite bandwidth. This limitation results in spreading of the pulse edges over time.
Superposition of Pulse Responses
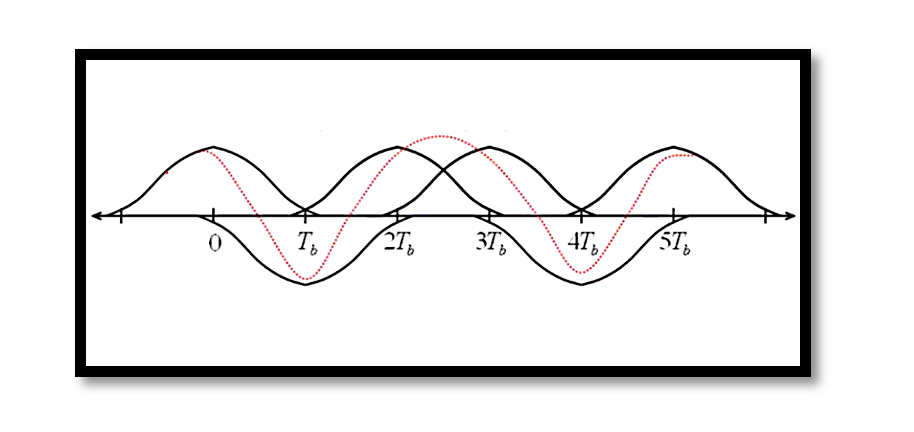
- For an input data stream of consecutive binary bits, the transmitted signal consists of multiple pulses. At the channel output, the pulses overlap due to their broadening. This phenomenon is illustrated in the second slide, where overlapping pulses create a superimposed signal waveform.
- This overlap leads to a problem called Inter-Symbol Interference (ISI), where the signal of one bit interferes with neighboring bits, complicating the receiver’s ability to interpret the data correctly.
Superposition of Pulse Responses
- For an input data stream of consecutive binary bits, the transmitted signal consists of multiple pulses. At the channel output, the pulses overlap due to their broadening. This phenomenon is illustrated in the second slide, where overlapping pulses create a superimposed signal waveform.
- This overlap leads to a problem called Inter-Symbol Interference (ISI), where the signal of one bit interferes with neighboring bits, complicating the receiver’s ability to interpret the data correctly.
Inter-Symbol Interference: A Critical Challenge
Inter-Symbol Interference is a form of distortion where the response of one transmitted bit spills over into adjacent bits.
- Each transmitted bit generates an individual pulse response.
- Due to pulse broadening, the responses for adjacent bits overlap, creating ambiguity at the receiver.
- Sampling the signal at incorrect points further exacerbates this issue.
The presence of ISI reduces the clarity of the received signal, increasing the probability of bit errors.
Impact of Signal Distortion on Data Transmission
Distortion and Inter-Symbol Interference can lead to data errors at the receiver:
- The receiver compares the received signal to a threshold (called the slicing level) to determine whether the transmitted bit was a ‘1’ or a ‘0.’
- If the distortion pushes the signal amplitude above or below the slicing level incorrectly, the receiver interprets the bit wrongly, resulting in an errored zero or an errored one.
Mitigating Signal Distortion and inter-symbol interference
To combat signal distortion and inter-symbol interference, several techniques are employed in communication systems:
- Pulse Shaping Filters: These filters (e.g., raised-cosine filters) are designed to minimize pulse spreading and inter-symbol overlap.
- Equalization: Adaptive equalizers at the receiver correct the channel-induced distortion by compensating for ISI.
- Error Correction Codes: These codes detect and correct errors at the receiver to ensure reliable data transmission.
- Increased Sampling Accuracy: Synchronizing the receiver’s sampling clock to the transmitted signal reduces the likelihood of sampling errors.
Take our entry level course (Below) for free using coupon code RAHRF101BLOG
RF Fundamentals, Basic Concepts and Components – RAHRF101
For limited time take an additional 10% off of all our courses using coupon code RFCERT10
Rahsoft RF Certificate and courses
Conclusion
Signal distortion and inter-symbol interference are inevitable challenges in digital communication systems, but through advanced signal processing and error correction techniques, their impact can be mitigated. Understanding these phenomena is crucial for designing robust systems that deliver accurate and reliable data transmission.

Learn more about this topic by taking the complete course ‘Introduction to Modulation in Communication Systems Online Course – RAHRF152’. Watch the course videos for more detailed understanding. Also checkout other courses on RF system and IC design on https://rahsoft.com/courses/. Rahsoft also provides a certificate on Radio Frequency. All the courses offer step by step approach.