What is a Low IF receiver
Low IF Receivers
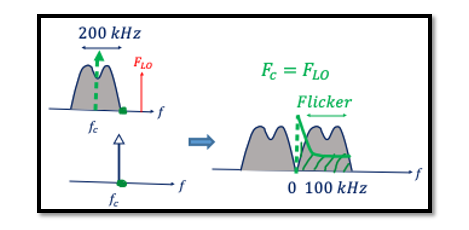
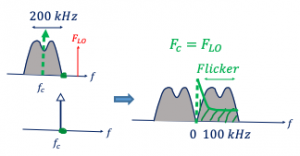
So far, we have discussed different kinds of receivers in our blogs, we talked about IF and zero IF receivers in intermediate or baseband however, we never discussed low IF receivers. Meaning we have the same IF receivers but this time the IF is lower. Low IF is somewhere between zero IF and IF receivers. As shown in the below diagram for low IF fLO is close to fc and near edge of the channel. We’re assuming that we have a direct conversion here, so assume that we have the local oscillator in the middle of our channel, therefore fLO is equal to fc in direct conversion. There’s another option where the fLO is right at the edge of this channel here, this is called low IF. In low IF there are some advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of Low IF:
- 1/f penalty is less severe in low IF
- Removing DC offset with high pass filter is feasible
The flicker noise at zero frequency is higher, so as you see in the zero IF this channel will be translated so the edge will be at the zero frequency. If you notice that the flicker noise has less effect on the part of our channel. This is one of the advantages, mostly we have a thermal noise effect on our channel in the low IF. What is flicker noise? and read about the types of noises in RF devices?
The drawback of direct conversion receiver is DC offset. DC offset is coming from local oscillator leakage. The local oscillator leakage problem causes large DC offset in the base band and saturates the baseband circuits. Removing the DC offset with high pass filter is feasible in low IF, as there is no data around zero frequency. Read more about DC offset.
Disadvantages of Low IF:
- Image problem as its not zero IF
- Suitable for narrow channel standards only
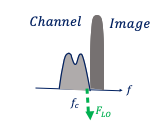
Low IF has some disadvantages, in absence of zero IF there will be image problem in the receiver. For example this diagram we have our channel and image, and frequency of local oscillator is between these two and they are at same distance from fLO. So this will be kind of image problem for us again. Read about image signal and effect of image for different LO frequencies here.
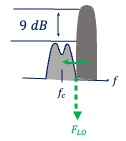 It’s very important we say that this type of system is used for narrow channel standards. For example one of the structures that is used for GSM receiver. The interferer is really close to our channel, for example GSM is 200 kHz and it’s nine above the channel so for example if you have an image rejection ratio (IRR) of 30 it’s enough for us. For this kind of receiver structure moderate IRR is enough, high IRR is not required. This can be said as one of the advantages of the low IF.
It’s very important we say that this type of system is used for narrow channel standards. For example one of the structures that is used for GSM receiver. The interferer is really close to our channel, for example GSM is 200 kHz and it’s nine above the channel so for example if you have an image rejection ratio (IRR) of 30 it’s enough for us. For this kind of receiver structure moderate IRR is enough, high IRR is not required. This can be said as one of the advantages of the low IF.
Low IF receivers are commonly used for a GSM receiver and as we know that for a GSM application the channel is narrow (200kHz) so it is kind of narrow band application.