Understanding Bit Rate, Baud Rate, and Their Importance in Communication Systems
In modern digital communication systems, data transmission is an integral aspect that ensures seamless connectivity and information sharing. Two key metrics that dictate the efficiency and speed of data transmission are bit rate and baud rate. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct aspects of the communication process. This blog delves deep into their definitions, differences, and their practical significance in communication systems.
What is Bit Rate?
Bit rate is defined as the number of bits transmitted per second in a communication channel. It is a measure of how fast data can be sent or received over a medium and directly relates to the amount of information being transmitted. Essentially, the bit rate determines the speed of data flow in bits per second (bps). The formula for bit rate is as follows:
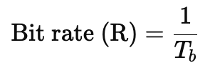
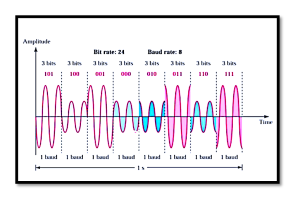
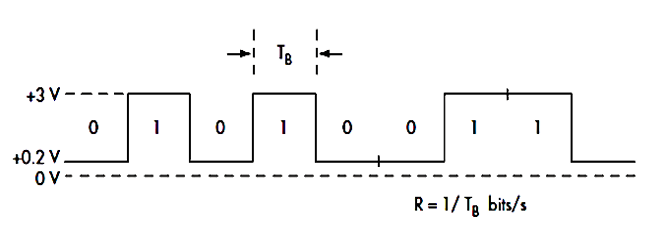
Here, Tb is the time duration for transmitting a single bit. A shorter Tb results in a higher bit rate, implying faster data transmission. For example, if Tb=1 ms, the bit rate will be 1000 bps, or 1 kbps. In the image shown a signal waveform is illustrated, where each interval of Tb represents a transition between binary digits (0s and 1s). These rapid transitions highlight how data is encoded in binary form, with the bit rate determined by the frequency of these transitions.
What is Baud Rate?
Baud rate refers to the number of signal units transmitted per second. Unlike bit rate, which deals with the number of bits, baud rate focuses on the symbols or signal units sent through the channel. Each signal unit may represent one or more bits, depending on the modulation scheme employed. The relationship between bit rate and baud rate is given by:
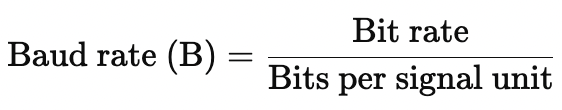
For instance, consider a scenario where each signal unit represents 4 bits. If the baud rate is 1000 symbols per second, the corresponding bit rate would be:
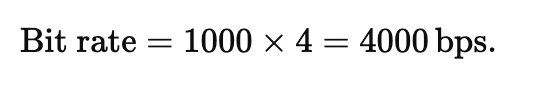
A Practical Analogy: The Highway Illustration
To better understand the distinction between bit rate and baud rate, let’s consider the analogy of a highway.
- Bandwidth: Think of the highway’s width as the channel’s bandwidth. A wider highway can accommodate more cars (signal units) simultaneously.
- Baud rate: Imagine the cars themselves as the signal units. The baud rate represents how many cars pass a certain point per second.
- Bit rate: The passengers in the cars represent the data being transmitted. If each car (signal unit) carries more passengers (bits), the bit rate increases while keeping the baud rate constant.
This analogy illustrates how bandwidth and modulation schemes play a critical role in determining both the bit rate and baud rate.
Simple vs. Complex Signaling
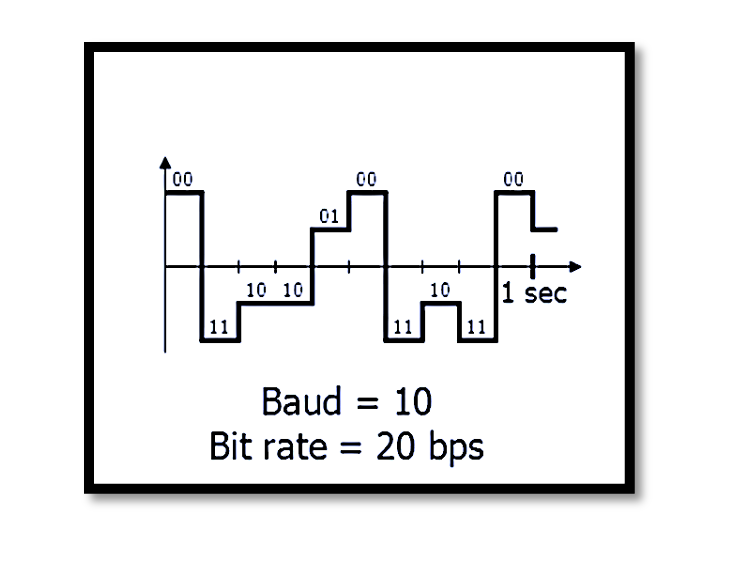
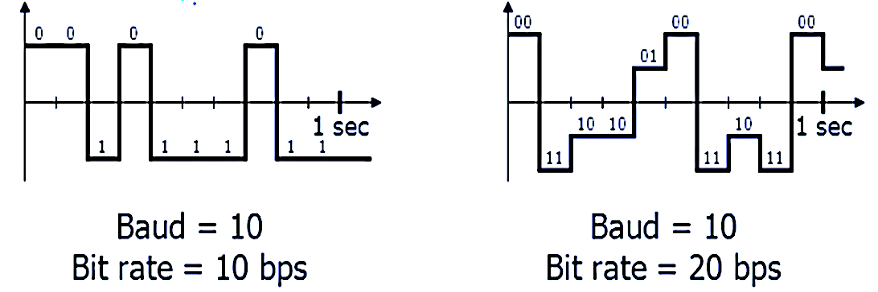
In simple signaling, each signal unit corresponds to one bit, making the bit rate equal to the baud rate. However, with complex modulation techniques, each signal unit can represent multiple bits, allowing for higher bit rates without requiring an increase in baud rate or bandwidth. The image showcases a comparison between simple and complex signaling, where a more advanced scheme achieves higher efficiency. For example, in a system with a baud rate of 10 symbols per second, using simple signaling results in a bit rate of 10 bps. On the other hand, employing a scheme where each signal represents 2 bits doubles the bit rate to 20 bps, all while maintaining the same baud rate.
Why It Matters: Applications in Communication
Understanding bit rate and baud rate is crucial for designing efficient communication systems, especially in bandwidth-constrained environments. Key applications include:
- Maximizing Bandwidth Utilization: By employing advanced modulation techniques, one can optimize the bit rate within limited bandwidth.
- Reducing Signal Interference: Intelligent use of baud rate ensures reliable data transfer even in noisy environments.
- Improving Transmission Efficiency: Modern systems like 4G/5G networks use these principles to balance speed and reliability.
Take our entry level course (Below) for free using coupon code RAHRF101BLOG
RF Fundamentals, Basic Concepts and Components – RAHRF101
For limited time take an additional 10% off of all our courses using coupon code RFCERT10
Rahsoft RF Certificate and courses
In conclusion, the interplay between bit rate and baud rate forms the backbone of digital communication systems. By comprehending these metrics, engineers can innovate and optimize systems to meet the demands of today’s fast-paced, data-driven world.

Learn more about this topic by taking the complete course ‘Introduction to Modulation in Communication Systems Online Course – RAHRF152’. Watch the course videos for more detailed understanding. Also checkout other courses on RF system and IC design on https://rahsoft.com/courses/. Rahsoft also provides a certificate on Radio Frequency. All the courses offer step by step approach.