Understanding Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) and Its Applications
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) is a widely used digital modulation scheme in modern telecommunications. It efficiently transmits data by combining both amplitude and phase variations of a carrier signal. QAM plays a crucial role in various communication systems, including wireless networks, broadband internet, and digital television.
What is QAM?
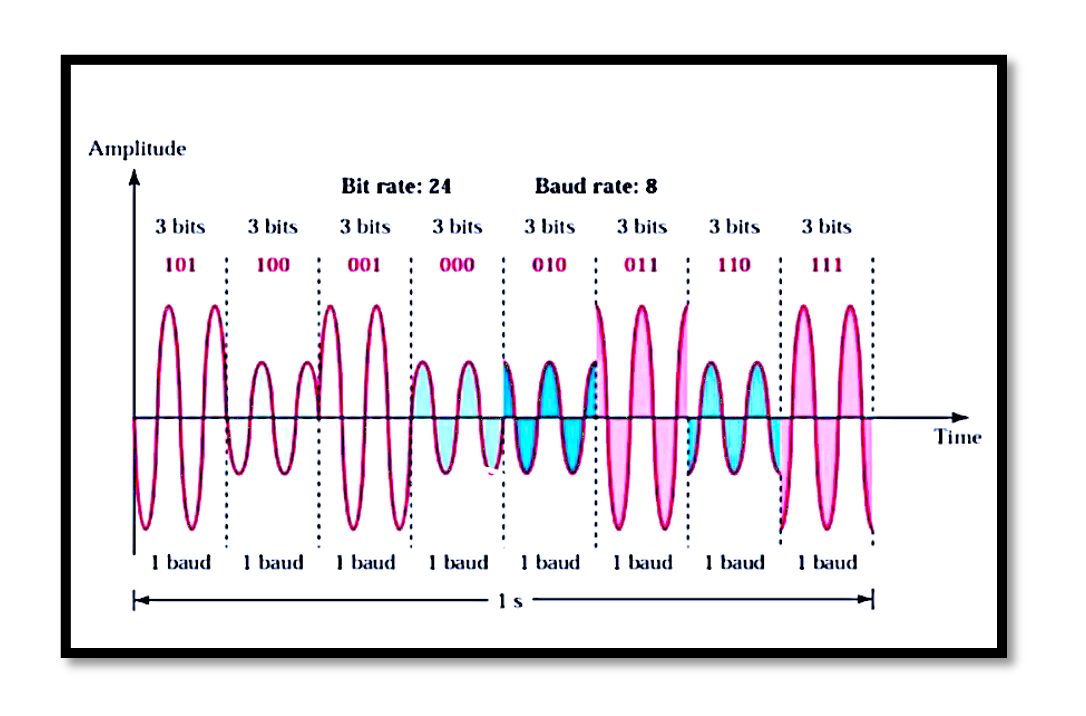
QAM is a modulation technique in which two carrier signals, shifted in phase by 90 degrees, are modulated independently and then combined. This results in a complex signal that exhibits variations in both amplitude and phase. By utilizing both amplitude and phase dimensions, QAM achieves higher spectral efficiency, allowing more bits to be transmitted per symbol. Mathematically, a QAM signal can be represented as:

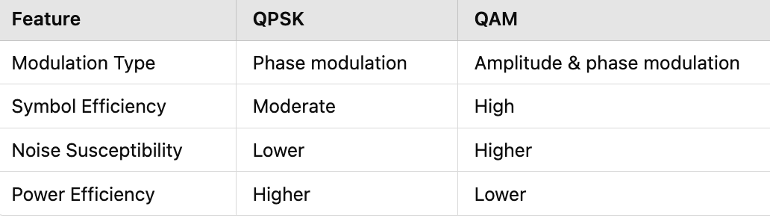
Difference Between QPSK and QAM
Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) is a special case of QAM where only phase variations occur, with no amplitude changes. In contrast, QAM allows for both phase and amplitude modulation, enabling higher data rates at the cost of increased susceptibility to noise.
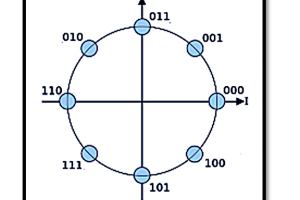
8-PSK vs. 8-QAM
In 8-Phase Shift Keying (8-PSK), the signal has eight distinct phase states, but the amplitude remains constant. However, in 8-QAM, the signal can have different amplitude levels in addition to phase variations. The primary difference between these two schemes lies in their efficiency and error performance:
- 8-PSK: Uses only phase shifts, making it more robust against amplitude noise but less efficient in terms of bandwidth usage.
- 8-QAM: Uses both amplitude and phase variations, allowing for a higher data rate but making it more susceptible to noise and requiring more linear amplification.
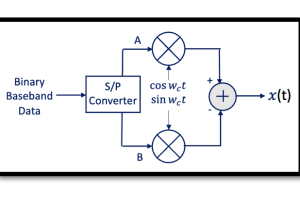
The provided block diagram illustrates an 8-QAM system, where the input data is split into I (in-phase) and Q (quadrature) components. A reference oscillator generates the carrier signal, which is modulated separately for each component before being combined to produce the final QAM signal.
Advantages and Disadvantages of QAM
Advantages:
- High Data Rate: QAM enables the transmission of more bits per symbol compared to purely phase-based modulation schemes like PSK.
- Efficient Bandwidth Utilization: By encoding multiple bits per symbol, QAM optimizes spectral efficiency.
- Versatility: Used in various applications, including Wi-Fi (802.11), cable modems (DOCSIS), and digital TV broadcasting.
Disadvantages:
- Susceptibility to Noise: The closer spacing of QAM states makes it more vulnerable to noise and signal degradation.
- Higher Power Requirements: Since QAM requires linear amplification, it consumes more power, making it less suitable for mobile devices.
- Complex Receiver Design: QAM demodulation is more complicated compared to simpler modulation techniques like BPSK or QPSK.
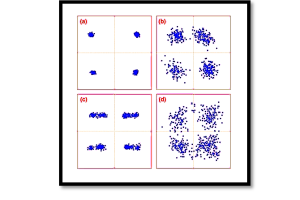
Detectability in QAM Systems
The performance of a QAM system depends on how well the receiver can distinguish between different symbols despite channel impairments such as noise, fading, and interference. Detectability is influenced by:
- Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR): Higher SNR improves demodulated signal quality.
- Channel Attenuation: Affects how well QAM symbols are received and decoded.
- Error Correction Techniques: Advanced techniques such as Forward Error Correction (FEC) improve reliability.
Take our entry level course (Below) for free using coupon code RAHRF101BLOG
RF Fundamentals, Basic Concepts and Components – RAHRF101
For limited time take an additional 10% off of all our courses using coupon code RFCERT10
Rahsoft RF Certificate and courses
Conclusion
QAM is a powerful modulation scheme that balances spectral efficiency and data rate, making it essential for modern digital communication systems. However, its susceptibility to noise and high power requirements pose challenges, particularly in wireless applications. As technology evolves, advanced error correction and adaptive modulation techniques help overcome these limitations, ensuring QAM remains a cornerstone of high-speed data transmission.

Learn more about this topic by taking the complete course ‘Introduction to Modulation in Communication Systems Online Course – RAHRF152’. Watch the course videos for more detailed understanding. Also checkout other courses on RF system and IC design on https://rahsoft.com/courses/. Rahsoft also provides a certificate on Radio Frequency. All the courses offer step by step approach.