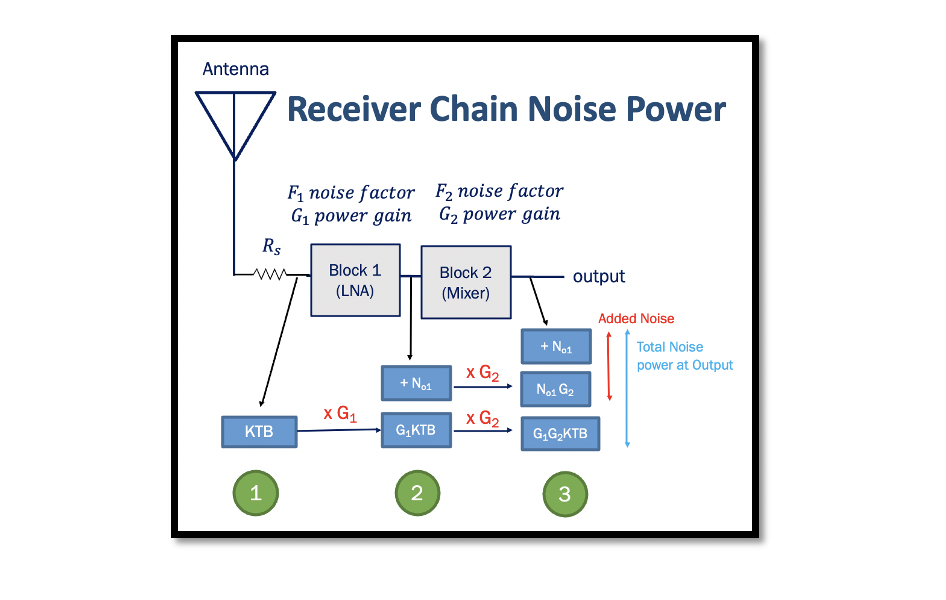
Example 2: Calculate the total NF for the below-given diagram: To calculate the total noise figure for this cascaded stage, we’re going to calculate the total noise factor. The linear expression for total noise factor is equal to the noise …
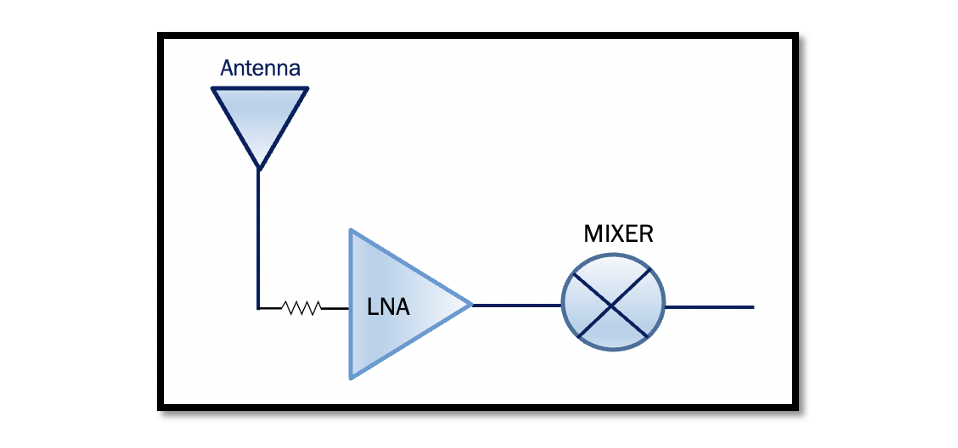
Example 1: Calculate the following for the below given RF circuit: Total Noise Figure (NF) of the system Input noise floor (Bandwidth = 5 MHz) Total PIIP3 Important points to remember: As you can see from the given inputs, the …
Noise Floor: The noise floor is the input-referred total noise power. If we have total noise at the output, we can refer it to the input. Total noise power means that the noise power of the Rs and the noise …
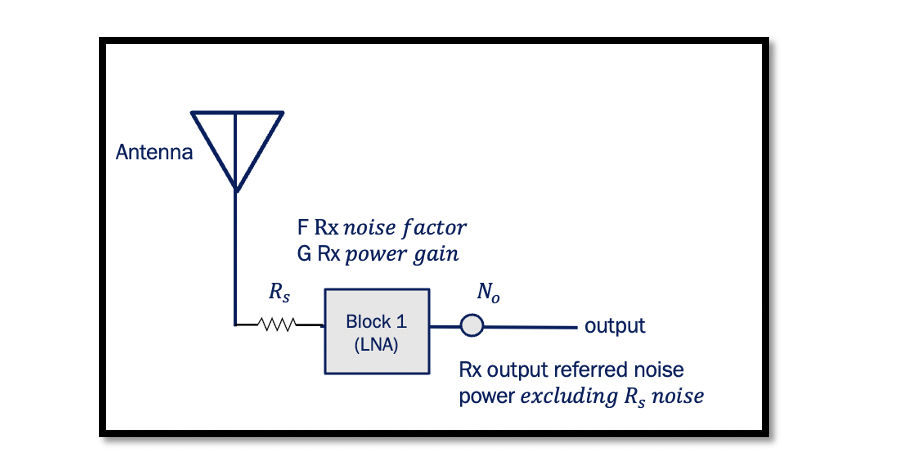
Input Noise Power Calculation For the below diagram, we need to calculate the noise power at the input of the receiver. So assume the given block is our receiver. It can be an LNA or any other block-like bandpass filter. …
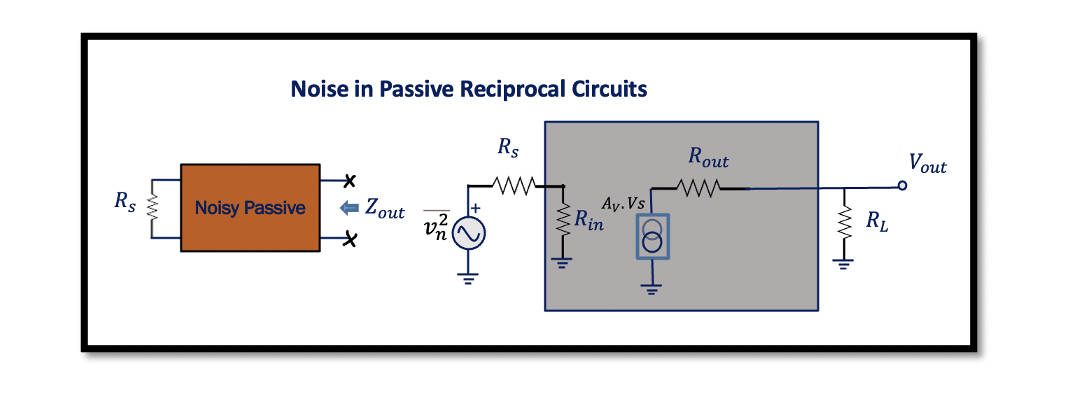
The network that consists entirely of linear passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors is usually called reciprocal. As it has passive elements, it’s a passive circuit, and it doesn’t have a transistor. The above figure shows an example consisting …
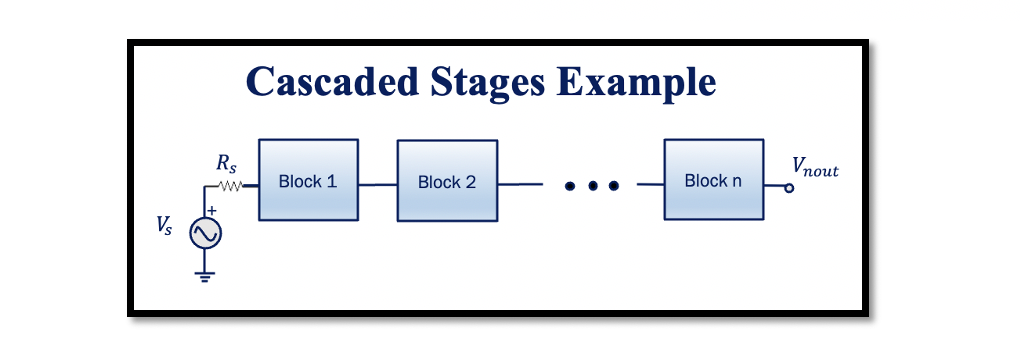
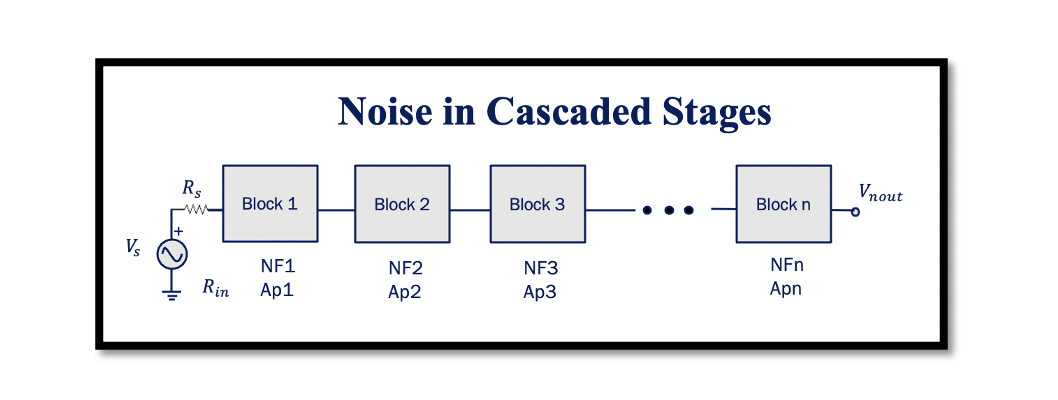
The concept of noise in cascaded stages is similar to that of linearity, where the aim was to find the total IIP3. Read about Non-linearity in Cascaded stages. Here we need to find the total Noise Figure, NF. If we …
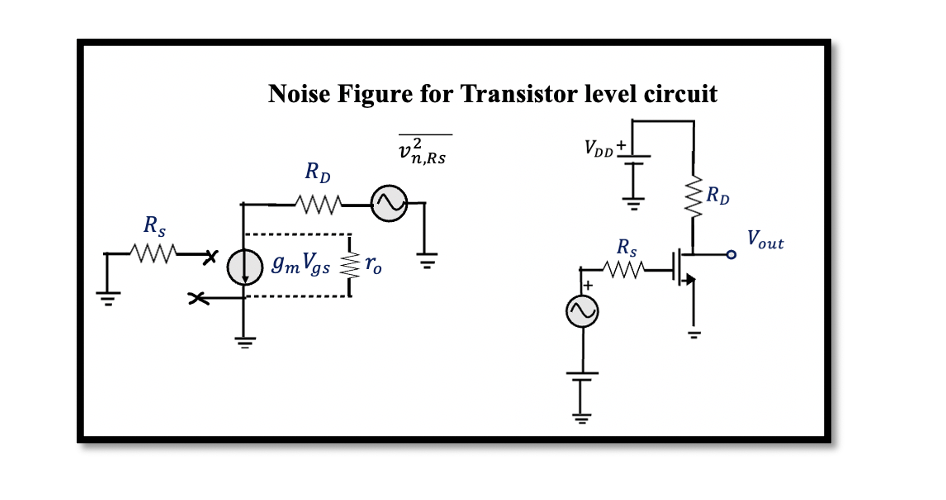
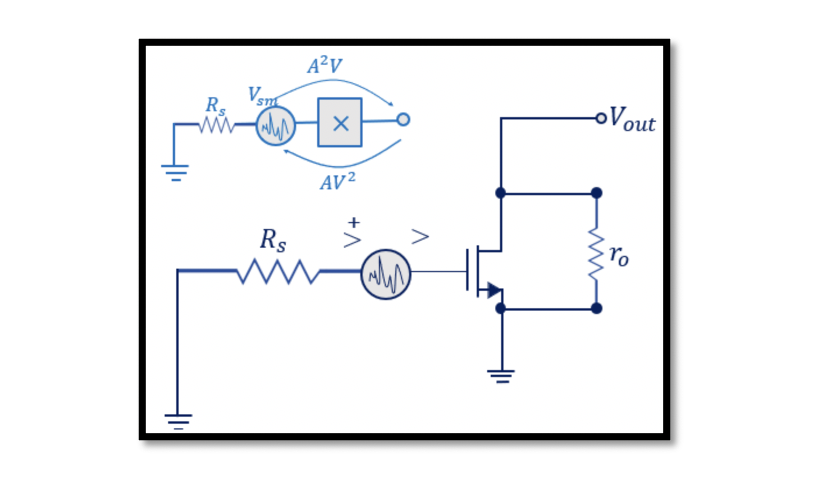
Find the NF for 1 stage transistor Assume this to be a simple amplifier circuit. At the input, we have source Vs and source resistance Rs. We have a MOS transistor in this circuit. Read more about the MOS transistor …
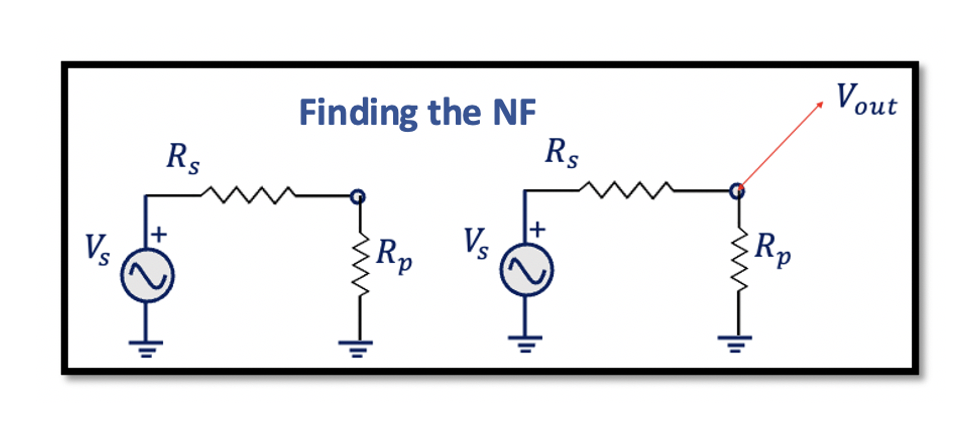
Find the Noise Figure for the given circuit This circuit consists of source Vs and two resistors Rs and Rp. Rs is the source resistance, and Rp is the parallel resistance. The noise effect at the output of the circuit …
How to find Input Referred Noise in the given circuit? Read about input-referred noise. In the below circuit diagram, Vs is the source, and Rs is the resistance of the source. R0 represents the short channel. IB is the bias …
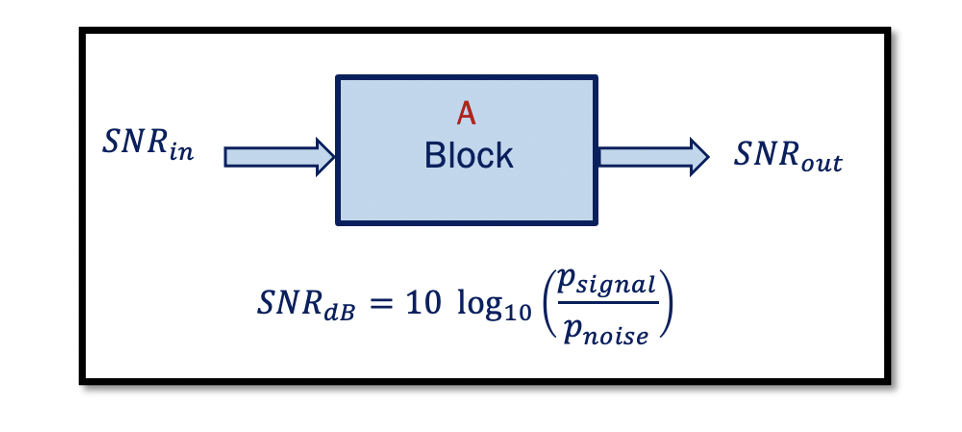
What is SNR? SNR is the Signal to Noise Ratio. Signal to noise ratio compares the level of the desired signal to the level of background noise. It can be shown as the ratio between the power of the signal …