Introduction Low Noise Amplifiers (LNAs) are crucial components in RF and microwave systems, primarily used to amplify weak signals without significantly degrading the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). One of the key challenges in LNA design is ensuring proper biasing of the …
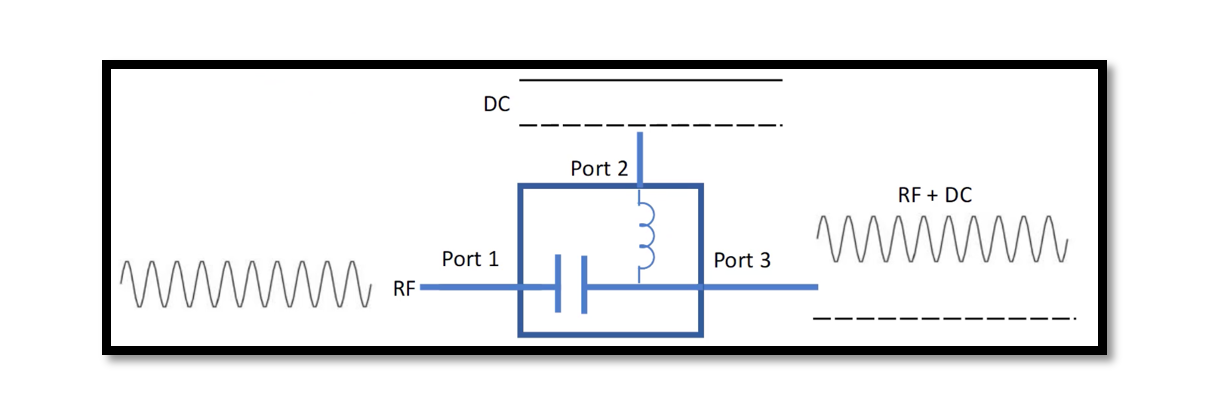
Introduction In RF (radio frequency) and microwave engineering, achieving precise impedance matching and signal control is paramount for the optimal performance of circuits and systems. One indispensable component that aids in this endeavor is the quarter-wave choke, often constructed using …
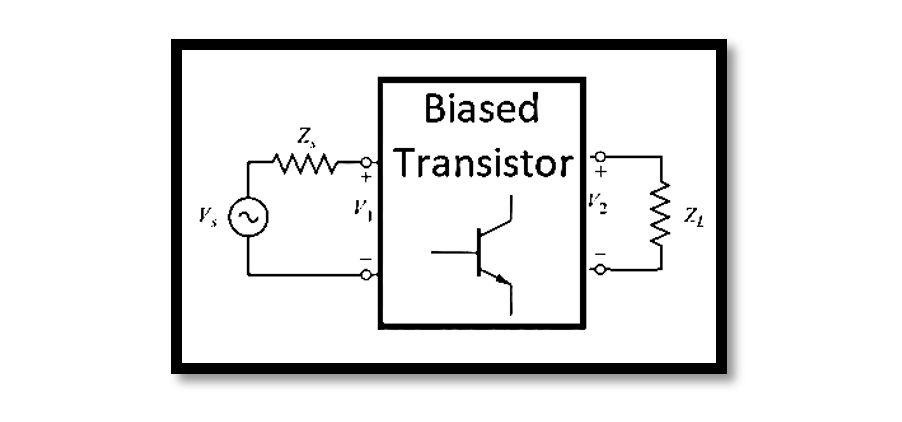
Transducer Power Gain and Available Power Gain Transducer Power Gain and Available Power Gain are two fundamental concepts in evaluating the efficiency of power transfer within networks. Available Power Gain (GA) serves as a crucial metric, representing the efficiency of …
Designing an LNA (Low-Noise Amplifier) for maximum gain is a critical aspect of RF and microwave circuit design. Achieving high gain is essential for amplifying weak signals while minimizing noise contributions. In this blog post, we will explore the design …
Importance of Stability: Stability is crucial in LNA design because it directly impacts the amplifier’s performance and reliability. Instability can lead to oscillations, which not only distort the signal but also cause potential damage to the amplifier and other components …
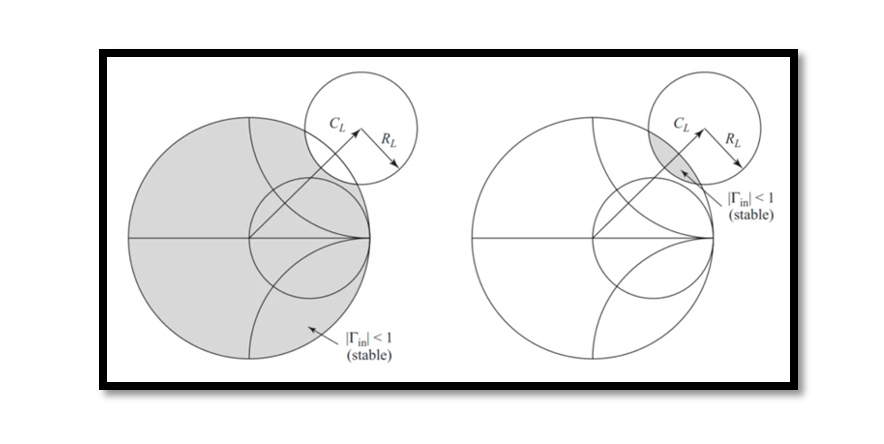
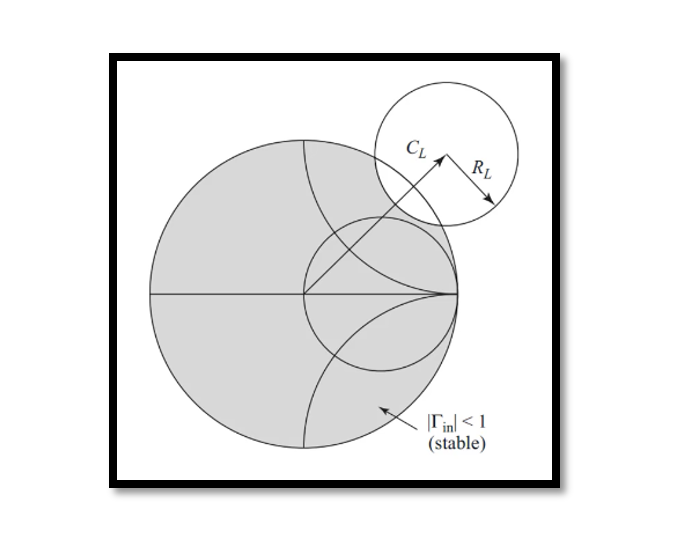
When it comes to designing Low-Noise Amplifiers (LNAs), ensuring stability is paramount. Stability refers to the amplifier’s ability to avoid oscillations, which can be detrimental to performance. Understanding stability types and the conditions under which an LNA remains stable is …
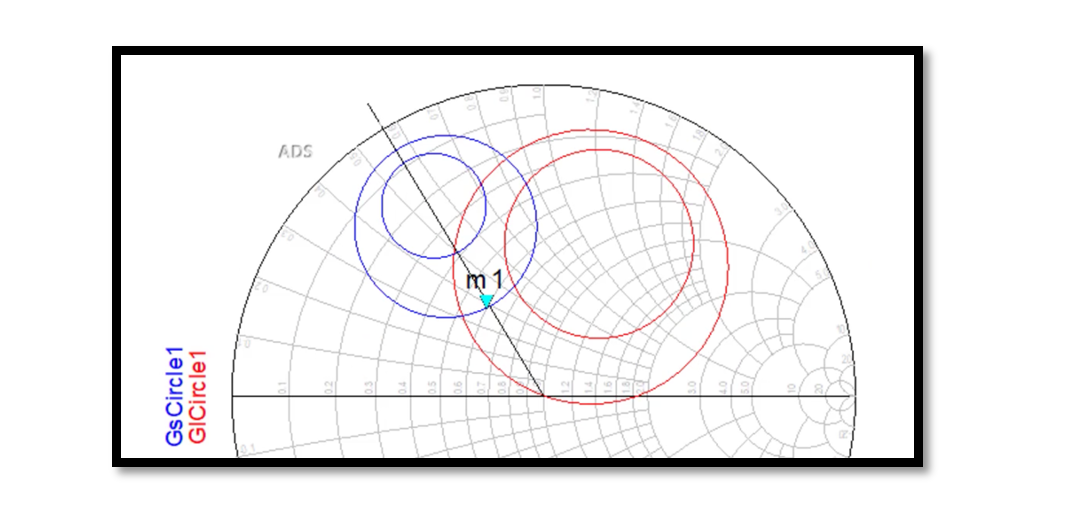
In the low noise amplifier (LNA) design, one of the critical metrics engineers grapple with is noise figure (NF). NF quantifies how much a device degrades the signal-to-noise ratio, crucial in applications where signal fidelity is paramount. Circles of Constant …
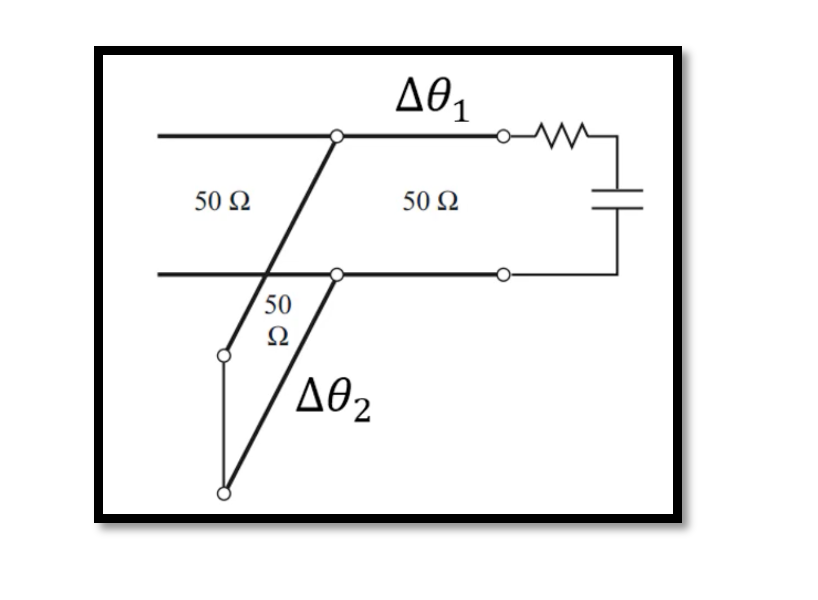
In the intricate world of RF circuit design, achieving optimal performance in Low Noise Amplifiers (LNAs) demands a thorough understanding of every component’s function and placement. Among these components, degeneration capacitors stand as pivotal elements, wielding significant influence over the …
Understanding the General Circuit At its essence, the General Circuit embodies a structured design philosophy aimed at optimizing performance across a spectrum of audio frequencies. Its architecture comprises several key elements meticulously arranged to ensure seamless signal processing. Let’s embark …
Microstrip lines stand as the backbone of modern high-frequency circuit design, offering a blend of performance and convenience. Yet, determining their precise dimensions can be akin to solving a puzzle. In this blog post, we’ll embark on a journey through …