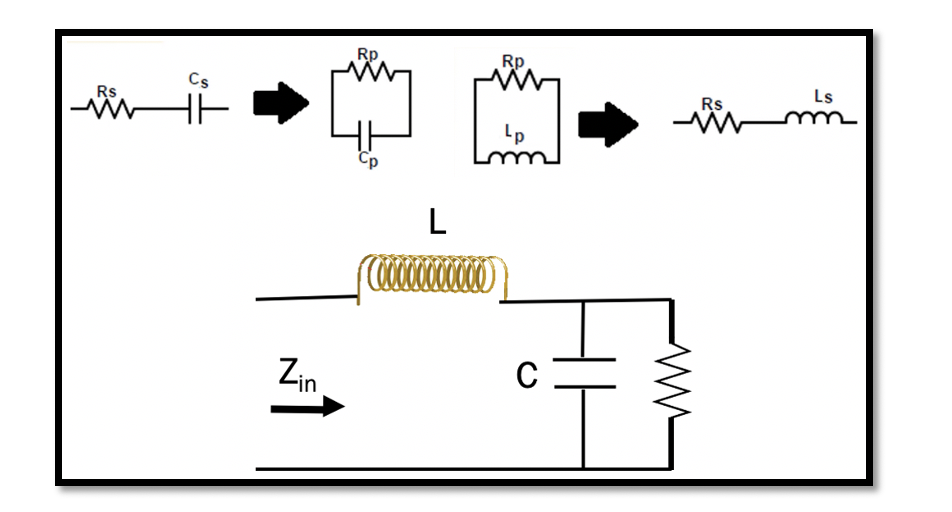
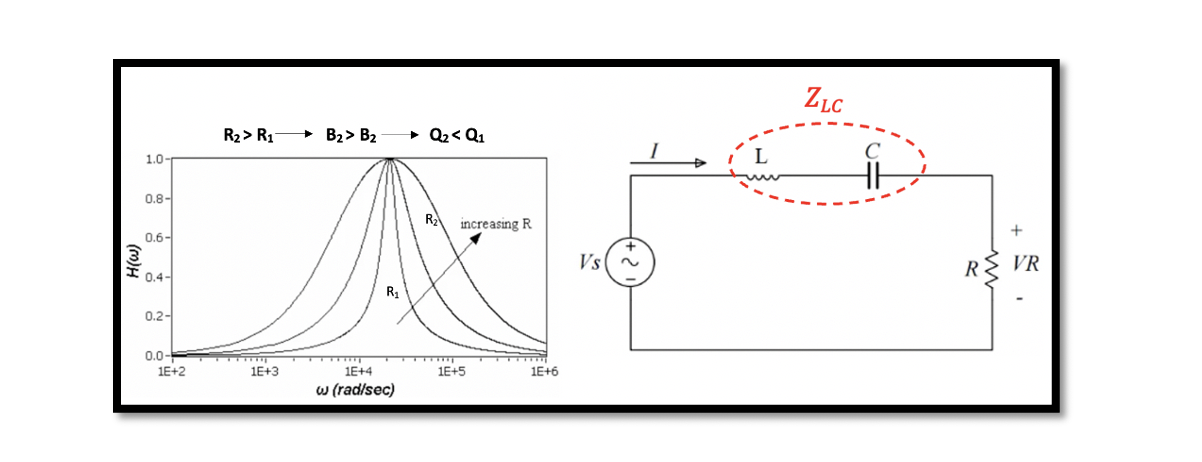
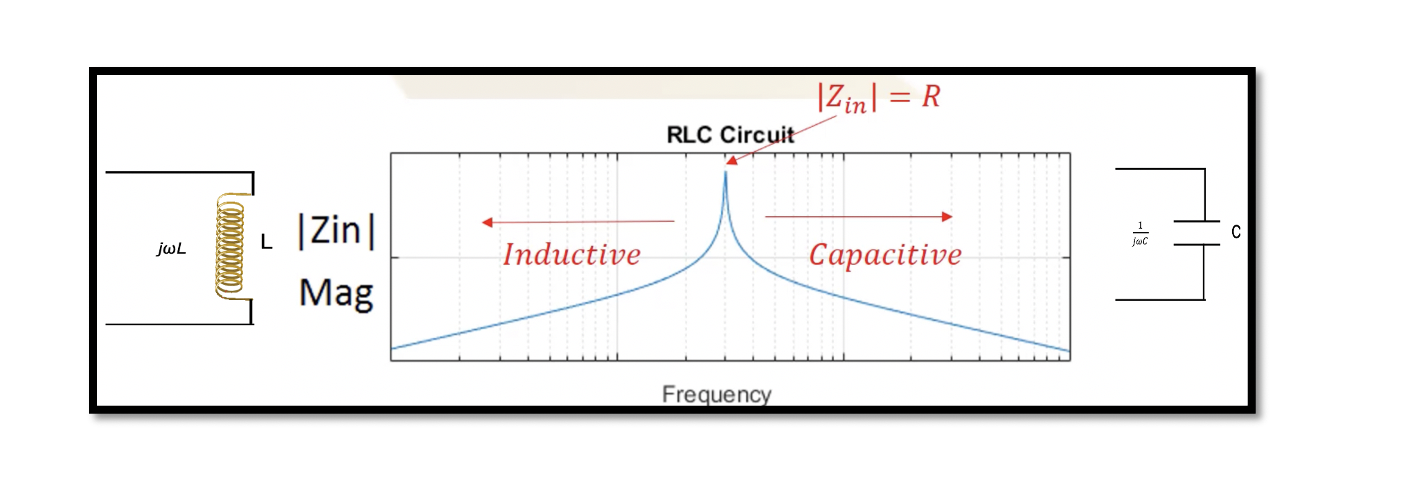
Resonance: Resonance in a RLC circuit is when we cancel out all the reactants in the circuit. In RLC circuit L & C are the reactants. So the reactances of inductance and capacitance are essentially cancelled out, and only resistance …
Defining the Transfer function for series RLC circuits Transfer function {H(w)} is equal to output voltage Vout divided by input voltage Vin which can be further written as: The graph represents the magnitude versus frequency. There are three different transfer …
In radio frequency systems, passive networks and passive circuits are used to match or transform impedance. Passive networks are also used to tune the RF blocks, obtain desired input and output impedance, and design different filters. Therefore, it is important …
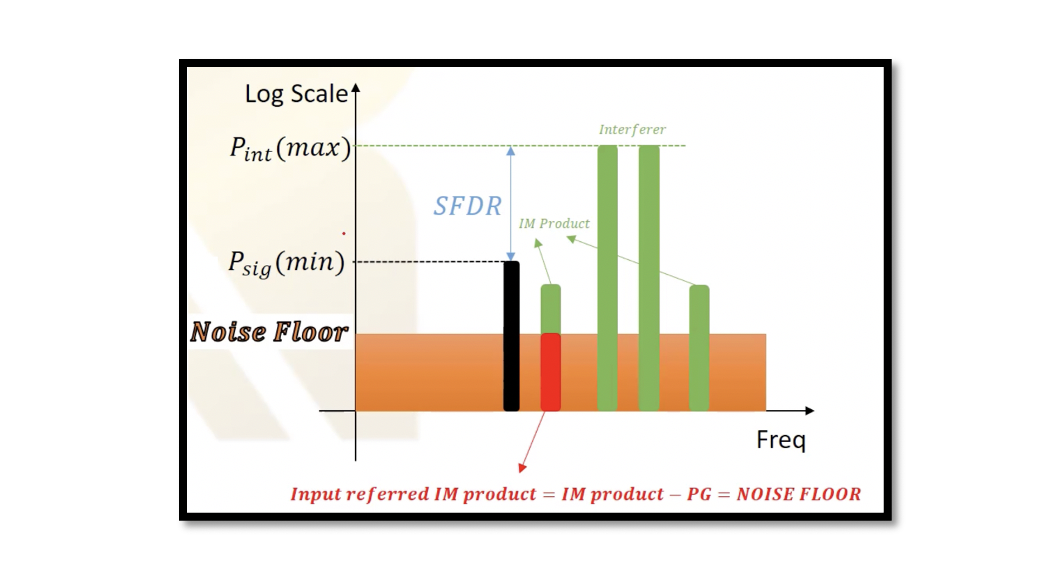
What is Dynamic Range? Dynamic range is the maximum input level that a receiver can tolerate divided by the minimum input level signal, which is defined as sensitivity. Dynamic range is equal to a maximum power of signal over minimum …
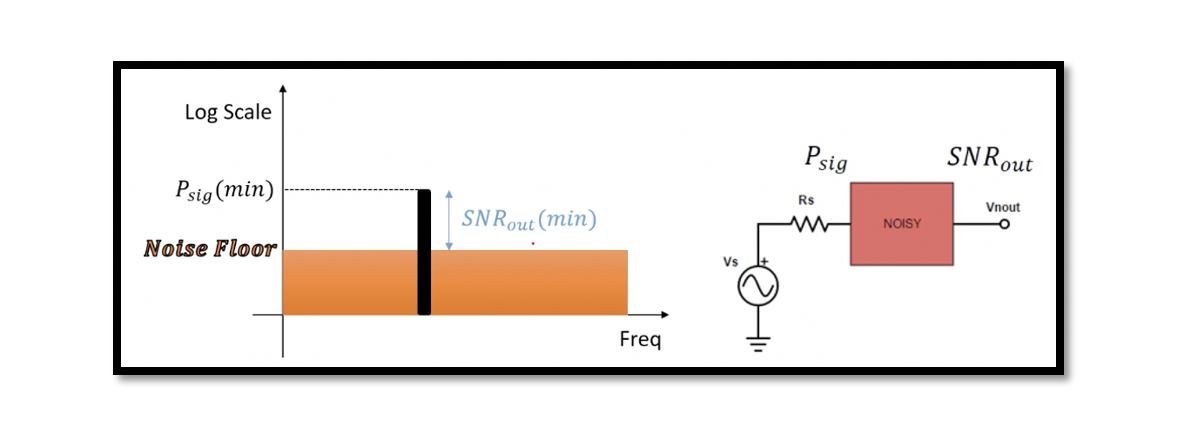
What is Radio Sensitivity? Sensitivity is the minimum signal which can be detected with accepted output SNR (Signal to Noise Ratio). Accepted output SNR is sometimes called as the minimum output SNR (SNRo, min). It means we are not allowed …
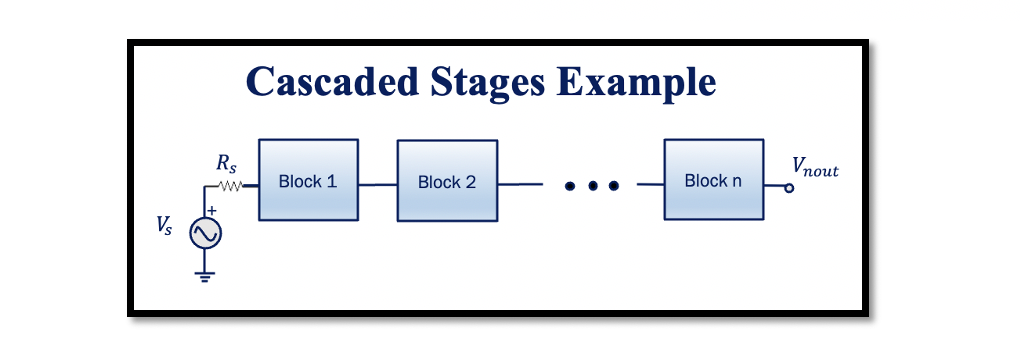
Example 2: Calculate the total NF for the below-given diagram: To calculate the total noise figure for this cascaded stage, we’re going to calculate the total noise factor. The linear expression for total noise factor is equal to the noise …
Example 1: Calculate the following for the below given RF circuit: Total Noise Figure (NF) of the system Input noise floor (Bandwidth = 5 MHz) Total PIIP3 Important points to remember: As you can see from the given inputs, the …
Noise Floor: The noise floor is the input-referred total noise power. If we have total noise at the output, we can refer it to the input. Total noise power means that the noise power of the Rs and the noise …
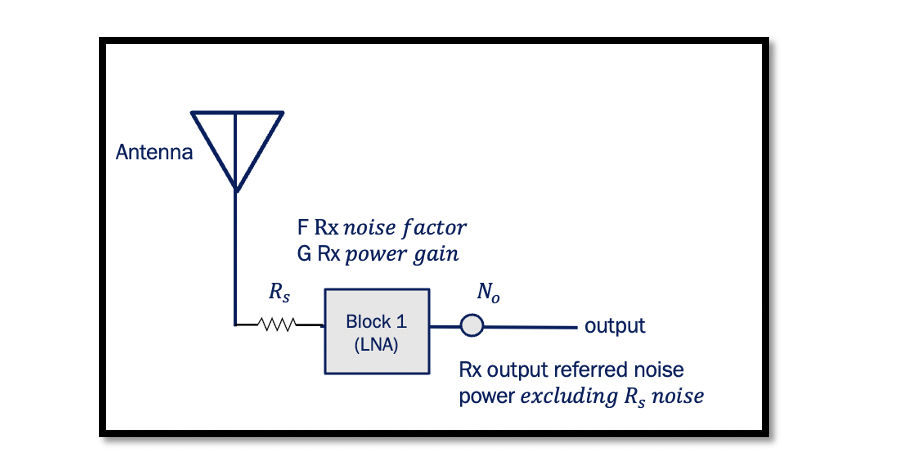
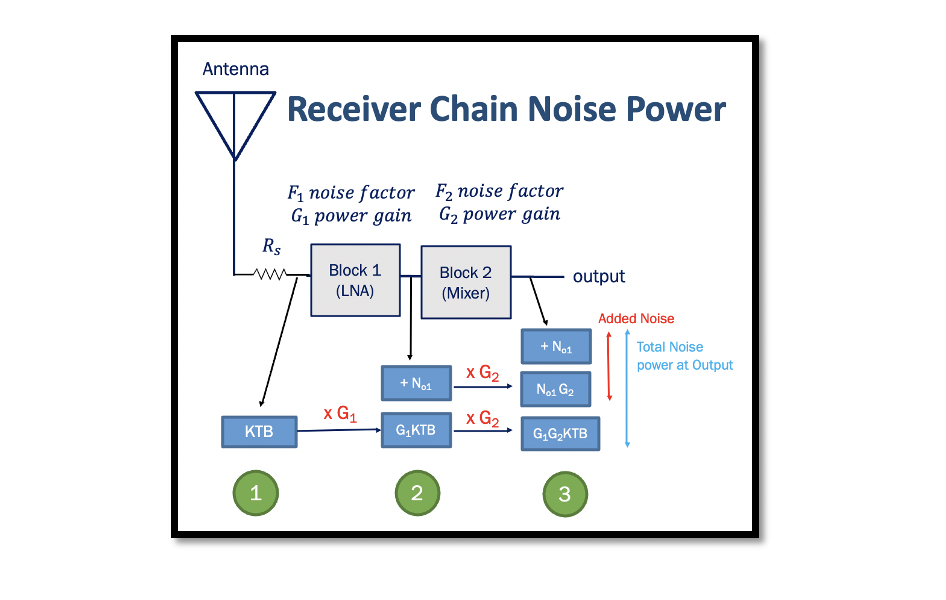
Input Noise Power Calculation For the below diagram, we need to calculate the noise power at the input of the receiver. So assume the given block is our receiver. It can be an LNA or any other block-like bandpass filter. …
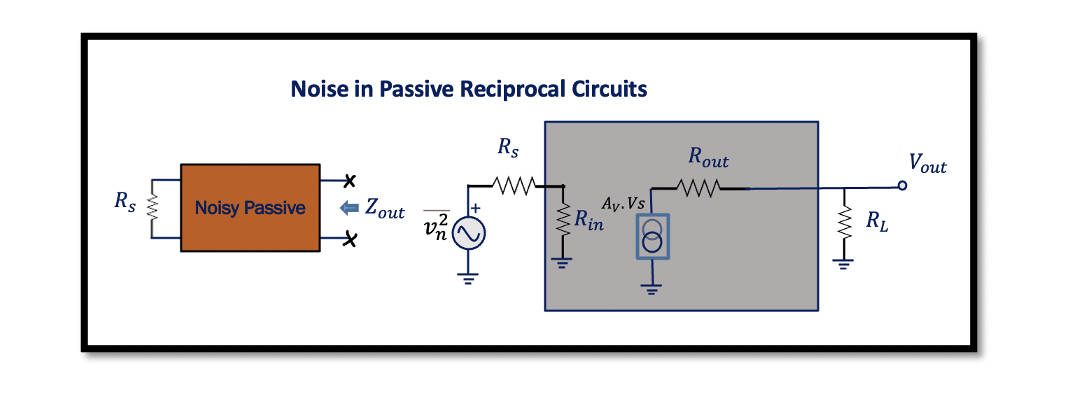
The network that consists entirely of linear passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors is usually called reciprocal. As it has passive elements, it’s a passive circuit, and it doesn’t have a transistor. The above figure shows an example consisting …