Power and Efficiency in Power Amplifiers
Power amplifiers are critical components in various electronic systems, playing a crucial role in boosting signal power to drive loads like speakers, antennas, and other devices. Understanding the power and efficiency of these amplifiers is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring energy-efficient operation.
Power and Efficiency Overview
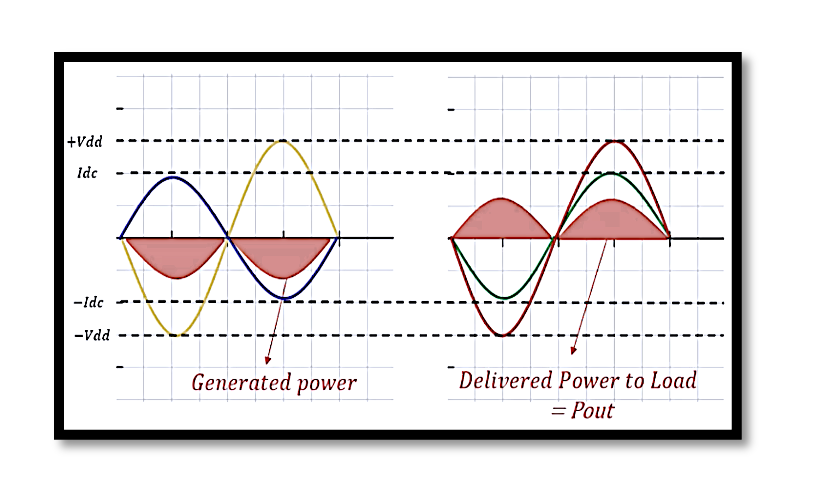
Generated Power and Delivered Power
The generated power and delivered power are fundamental concepts:
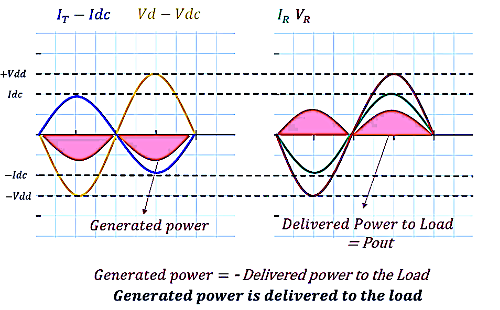
Generated Power (Pgen):
- Represented by the area under the IT−Idc and Vd−Vdc waveforms.
- The formula for generated power is given by:
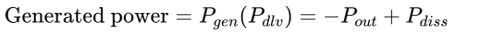
Delivered Power to Load (Pout):
- Illustrated by the area under the IR and VR waveforms.
- Delivered power is the actual power sent to the load.
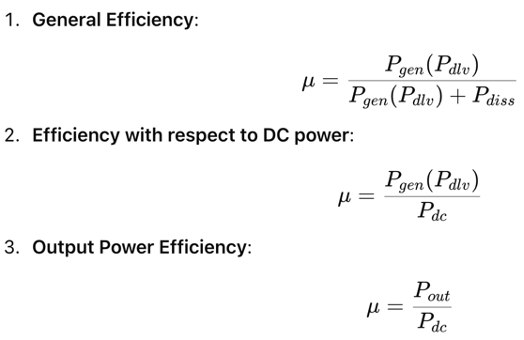
Efficiency Calculation
Efficiency (μ) of a power amplifier can be calculated using various formulas, as shown in the slides:
Power Formulas
Key power formulas are essential for calculating the output power and understanding the operation of power amplifiers:
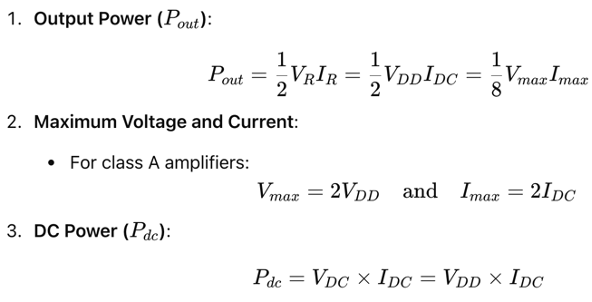
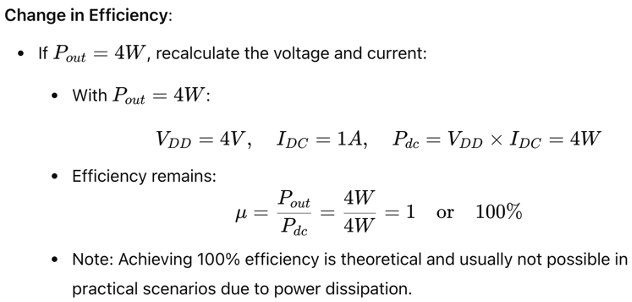
Example Calculation
Let’s apply these concepts to a specific example provided in the slides:
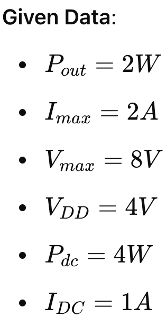

Practical Considerations in Power Amplifier Design
When designing power amplifiers, several practical considerations come into play that affect both power and efficiency. One significant factor is the Class of Operation. Power amplifiers are classified into different classes (A, B, AB, C, etc.) based on their conduction angle and operating point. Each class has distinct characteristics that impact efficiency and linearity:
- Class A Amplifiers: These amplifiers conduct for the entire cycle of the input signal, offering excellent linearity and signal fidelity. However, they are typically less efficient, with a theoretical maximum efficiency of around 25-30%, due to constant current flow even without input signal.
- Class B and AB Amplifiers: Class B amplifiers conduct for half of the input cycle, which improves efficiency (theoretically up to 78.5%) but can introduce distortion at the crossover point. Class AB amplifiers address this by conducting slightly more than half the cycle, balancing efficiency and linearity.
- Class C Amplifiers: These amplifiers conduct for less than half the input cycle, providing high efficiency (up to 90%) but are suitable mainly for applications like RF transmission where signal distortion is acceptable and can be corrected downstream.
Another key consideration is Thermal Management. Power dissipation in amplifiers generates heat, which must be effectively managed to maintain performance and prevent damage. This involves using heat sinks, cooling fans, and thermal compounds to dissipate heat away from sensitive components.
Load Impedance Matching is also crucial. Impedance mismatch between the amplifier and load can lead to power reflections, reduced power delivery, and potential damage to the amplifier. Proper impedance matching ensures maximum power transfer and minimizes signal loss.
Feedback Mechanisms are employed in amplifier design to improve performance characteristics such as stability, bandwidth, and linearity. Negative feedback, for instance, can significantly reduce distortion and increase the bandwidth of the amplifier, though it might slightly reduce the gain.
Power Supply Design is another critical aspect. A well-designed power supply ensures that the amplifier receives a stable and clean voltage, which is essential for maintaining signal integrity and preventing noise. The choice between linear and switching power supplies involves trade-offs between efficiency, noise, and cost.
By carefully considering these factors, engineers can design power amplifiers that not only meet the desired performance criteria but also operate efficiently and reliably in their intended applications. Balancing efficiency, linearity, thermal management, and impedance matching is key to achieving optimal amplifier performance.
Take our entry level course (Below) for free using coupon code RAHRF101BLOG
RF Fundamentals, Basic Concepts and Components – RAHRF101
For limited time take an additional 10% off of all our courses using coupon code RFCERT10
Rahsoft RF Certificate and courses
Conclusion
Understanding power and efficiency in power amplifiers involves analyzing the generated and delivered power and calculating the efficiency using various formulas. These concepts are crucial for designing energy-efficient amplifiers that deliver optimal performance.

Learn more about this topic by taking the complete course ‘Linear RF Power Amplifier (PA) Design Theory and Principles online course – RAHRF562’. Watch the course videos for more detailed understanding. Also checkout other courses on RF system and IC design on https://rahsoft.com/courses/. Rahsoft also provides a certificate on Radio Frequency. All the courses offer step by step approach.