Understanding Jitter and Phase Noise in Oscillators
Introduction
In electronic circuits, particularly those involving signal processing and communications, the stability and precision of oscillators are paramount. Two critical factors that affect the performance of oscillators are jitter and phase noise. This blog will explore these concepts in detail, drawing from the information and illustrations provided.
What is Jitter?
Jitter refers to the deviation in timing of a signal’s periodic events. It is essentially the variability in the cycle-to-cycle timing of a signal compared to its ideal timing. This deviation can have significant implications on the performance of electronic systems, particularly in high-speed digital circuits and communication systems.
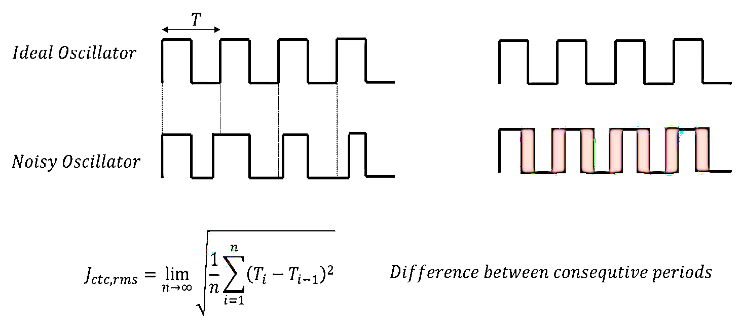
Types of Jitter
Cycle-to-Cycle Jitter: This is the time difference between consecutive cycles of a signal. It’s often measured as the root mean square (RMS) value of the time deviations between cycles.
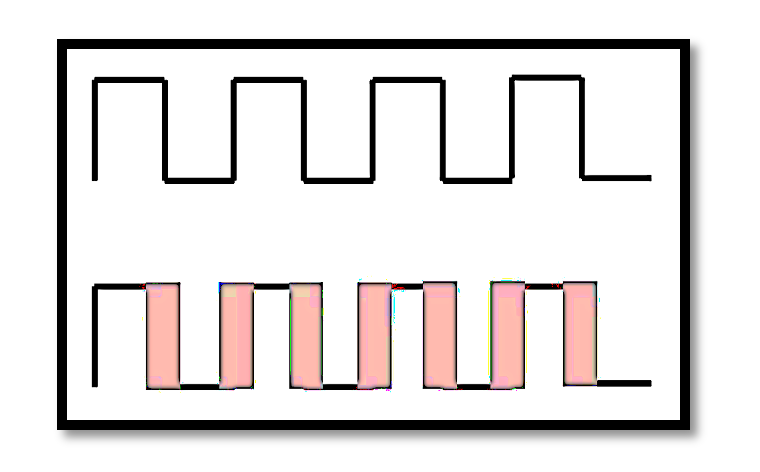
The ideal oscillator produces a perfectly periodic signal with a constant period TTT. In contrast, a noisy oscillator shows variations in its period, represented by the gray areas in the diagram. These variations result from random noise affecting the oscillator, causing deviations from the ideal timing.
Peak-to-Peak Jitter: This measures the maximum deviation between any two cycles within a given period.
What is Phase Noise? Phase noise refers to the rapid, short-term fluctuations in the phase of a signal, often viewed in the frequency domain. It is a critical factor in determining the spectral purity of oscillators and affects the performance of systems such as frequency synthesizers and communication links.

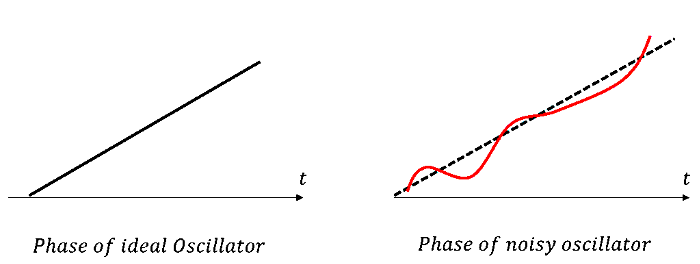
In the phase versus time plot, the ideal oscillator shows a linear phase progression (black line), while the noisy oscillator shows deviations due to random noise (red line). This randomness introduces errors in the timing of the signal, affecting the overall performance of the system.
Relationship Between Jitter and Phase Noise
Jitter and phase noise are closely related concepts. Jitter is the time domain representation of phase noise, which is typically analyzed in the frequency domain. The random jitter power is essentially the area under the phase noise spectrum.

According to Parseval’s theorem, the average power (which corresponds to the phase noise) is the area under the spectrum.
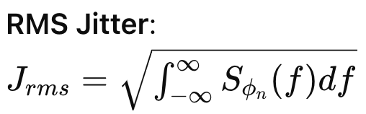
This relationship shows that the RMS jitter can be calculated from the integral of the phase noise power spectral density. Hence, minimizing phase noise will directly reduce jitter, leading to a more stable and precise oscillator.
Practical Implications
Understanding and controlling jitter and phase noise are crucial for designing high-performance electronic systems. Here are a few practical implications:
- Communication Systems: High jitter can cause bit errors in digital communication systems, leading to data loss or corruption.
- Clock Distribution: In high-speed digital circuits, such as those found in computers and networking equipment, jitter can lead to timing errors, affecting the overall performance of the system.
- Frequency Synthesizers: Phase noise impacts the purity of signals generated by frequency synthesizers, which are essential in applications like wireless communications and signal processing.
Take our entry level course (Below) for free using coupon code RAHRF101BLOG
RF Fundamentals, Basic Concepts and Components – RAHRF101
For limited time take an additional 10% off of all our courses using coupon code RFCERT10
Rahsoft RF Certificate and courses
Conclusion
Jitter and phase noise are fundamental parameters in the design and analysis of oscillators and related electronic systems. By understanding their origins, mathematical representations, and practical implications, engineers can better design systems that are robust, reliable, and high-performing. Reducing jitter and phase noise is c

Learn more about this topic by taking the complete course ‘Phase Lock Loop System Design Theory and Principles RAHRF469’. Watch the course videos for more detailed understanding. Also checkout other courses on RF system and IC design on https://rahsoft.com/courses/. Rahsoft also provides a certificate on Radio Frequency. All the courses offer step by step approach.
Tag:Jitter, Oscillators, Phase Noise