What are Transmission Lines and its relationship with Smith Chart? Transmission lines are a fundamental part of electrical engineering used to transmit electrical signals or power from one point to another efficiently. They’re composed of conductors and insulators and are …
Introduction In RF engineering, a powerful tool stands as a guiding light for designers and engineers is the Smith Chart. Born out of the necessity to streamline impedance matching and analysis in radio frequency circuits, this circular marvel has become …
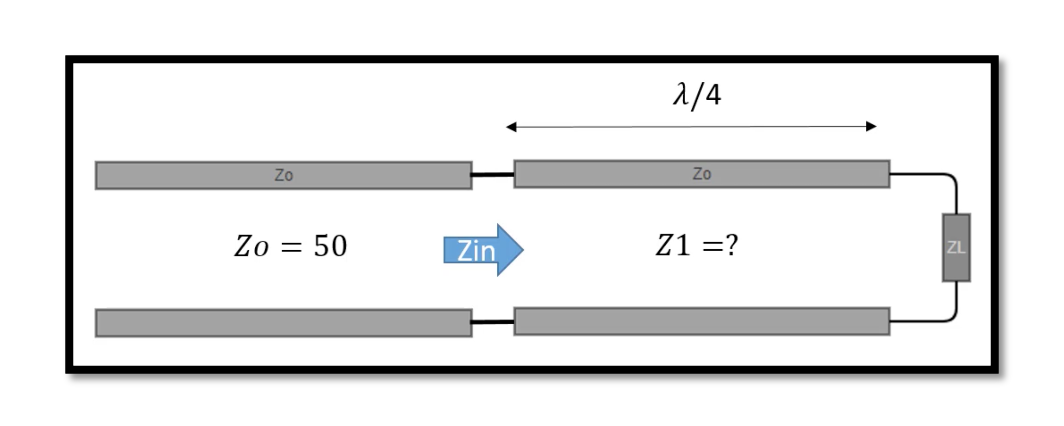
What is Quarter Wave Transmission Line? A quarter-wave transmission line has a characteristic impedance of Z0, which matches the impedance of the source and the load. The length of the quarter-wave line is chosen so that the impedance seen at …
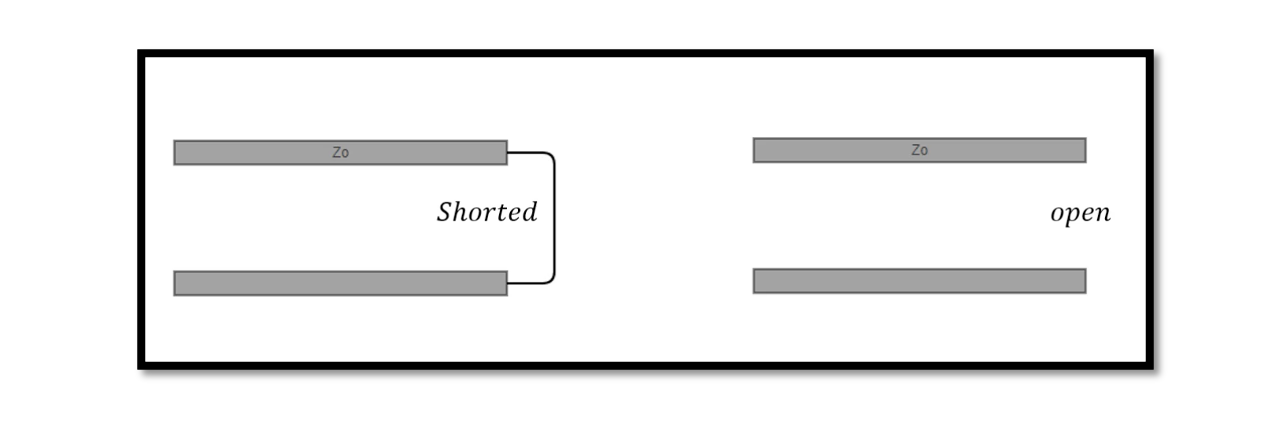
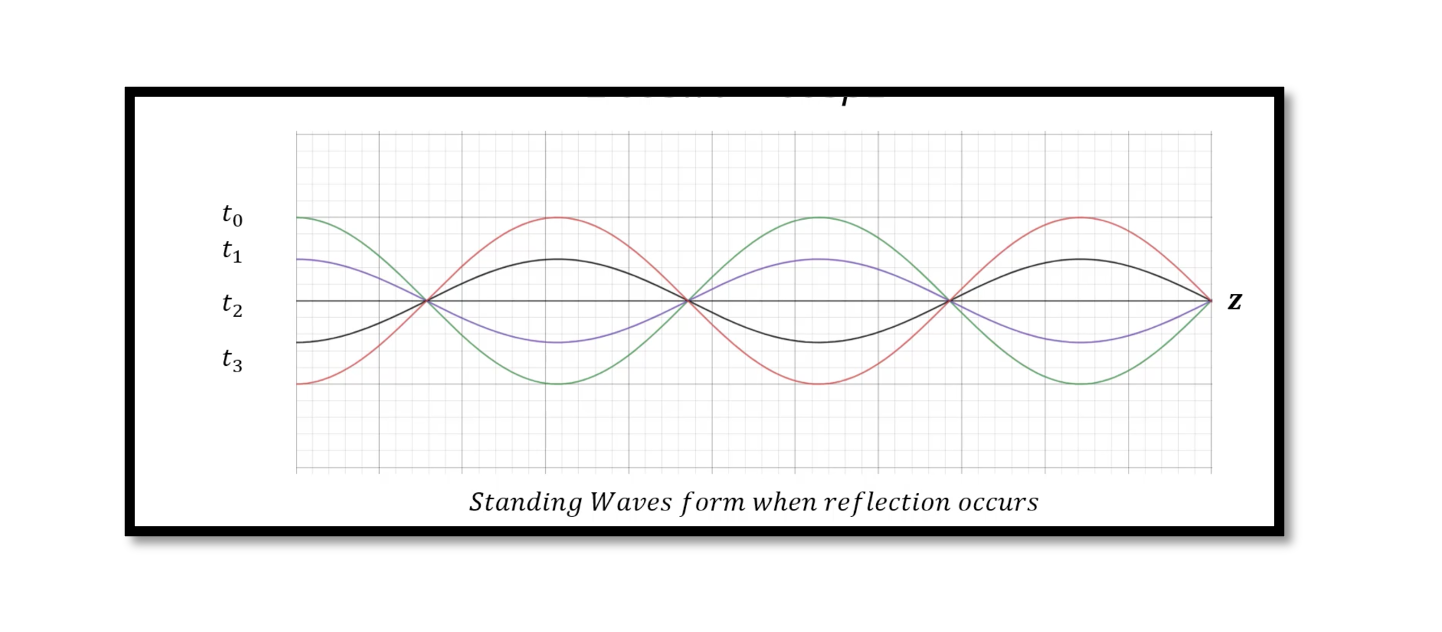
There are two special cases of lossless terminated lines which we will be discussing in this blog. Assume that one of the transmission lines is shorted at one end that means impedance ZL=0 and the other one is open at …
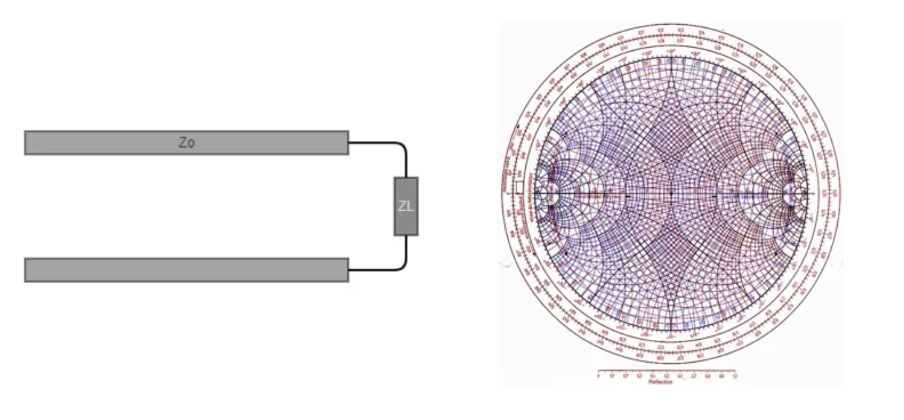
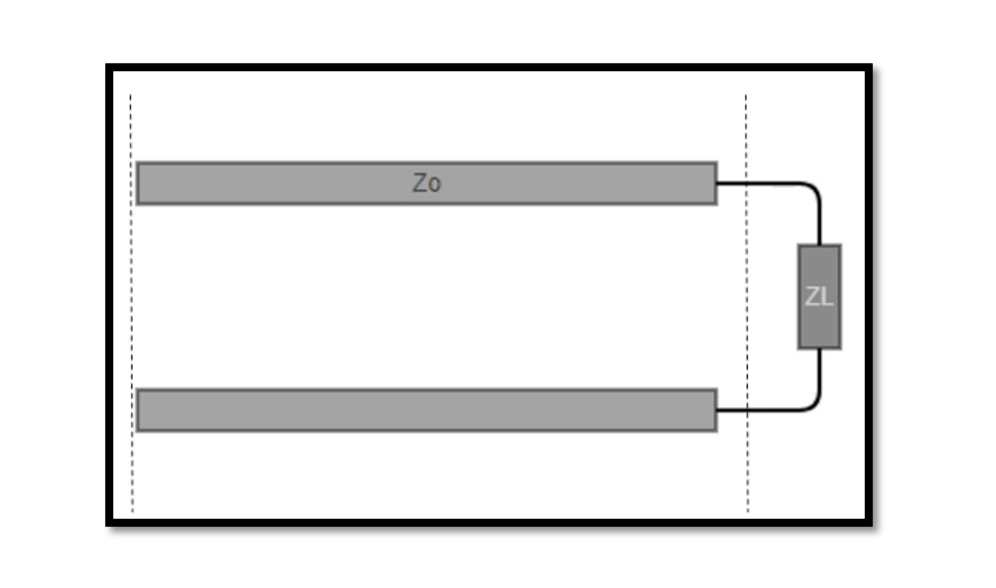
Transmission line terminated by a load Let’s consider a simple example of a transmission line terminated by a load. The transmission line consists of a pair of conductors (wires) separated by a dielectric material. At one end, the transmission line …
When does Reflection occur in Transmission Line? Impedance mismatch in transmission line can cause impedance mismatch which is the cause of reflection. A wave travelling through transmission will obviously face characteristic impedance. Read more about characteristic impedance. When there is …
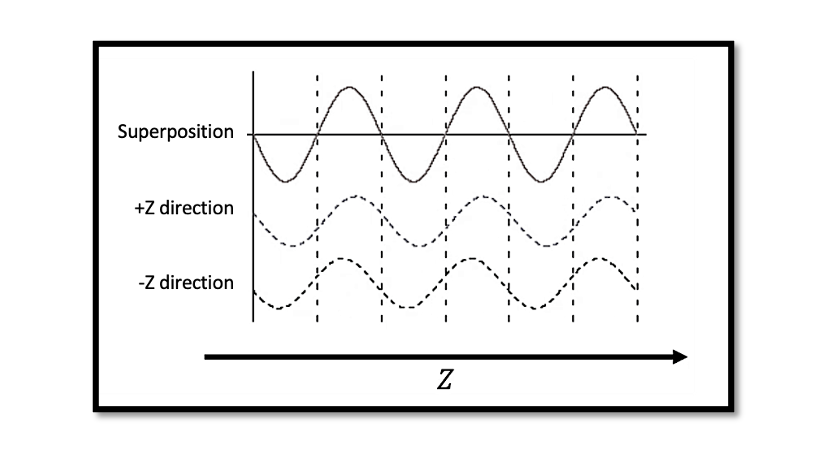
In the previous blogs, we discussed transmission line time domain equations using the phasor formula. In the first case assuming there is no reflection we showed wave propagation and second case we showed the condition of the standing waves when …
In the previous blog we discussed about Transmission Line Time Domain Equations where we showed how to convert the phasor equations to time domain equation and proved the wave propagation. Example to prove Reflection Voltage We have a lossless transmission …
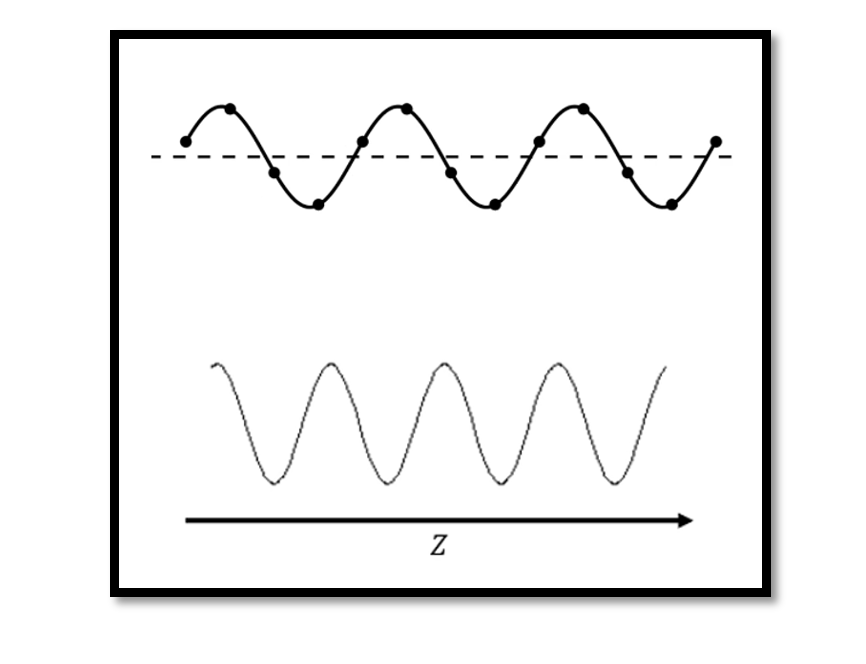
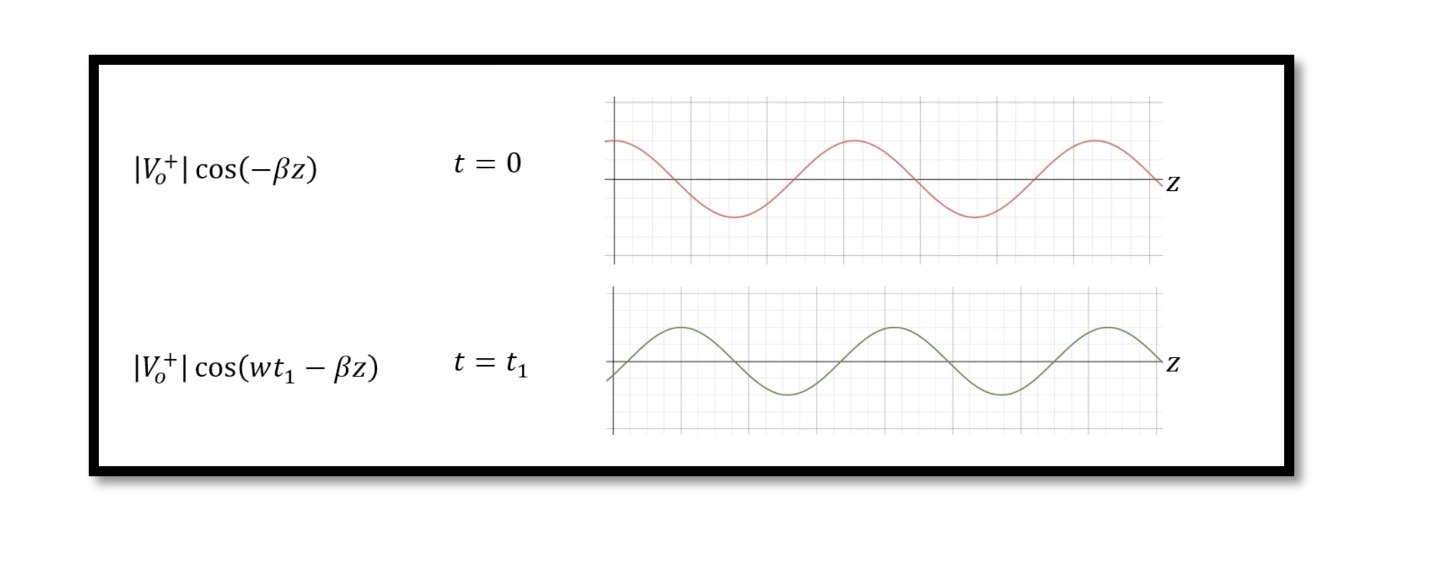
In previous blogs, we discussed about wave propagation where we said that the voltage on the transmission line will propagate and have wave like behaviour. In this section, we will prove this theory. We can understand the behaviour of voltage …
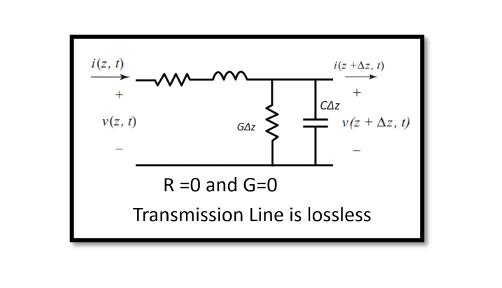
In a transmission line, the four primary distributed parameters are resistance (R), capacitance (C), inductance (I), and conductance (G). The secondary constants are the characteristic impedance (Zo) and complex propagation constant (y) that are derived using the primary parameters. Transmission …